Skeleton Keypoints
Darwin fundamentals
Darwin advanced

Play video
4:44

Play video
4:44

Play video
4:44
In this Darwin Fundamentals session, we explore the Keypoint Skeleton feature, a particularly useful tool for 2D image and video annotation. In simple terms, Keypoint Skeletons are sets of predefined points, joints, and shapes that can be adjusted to match an object’s pose. They’re an efficient way to define object poses or create custom polygons for reuse in projects.
Eager to explore keypoint annotation tools and tricks in more detail? Explore our guide to keypoints and skeletons.
In this video, we start by demonstrating how to create a Keypoint Skeleton for a human hand, mapping each point and joint to the fingers. From here, we explain how to change the Instance Tracking ID of each point, to make use of the Keypoint Skeleton simple for your use case.
Next, we explore how to use the Keypoint Skeleton within your datasets once it's been set up. We showcase how to drag and drop the Keypoint Skeleton onto your frame, manipulate it to an object, and adapt it per frame. We also explain how the Keypoint Skeleton tool behaves in video, showcasing how the tool interpolates between varying frames so you only have to label a few frames to get a smooth transition that represents ground truth.
We also note one important thing: the Keypoint Skeleton is versatile, and not limited to specific object types. For example, it can be used to create custom polygons, such as cuboids or pentagons, to represent different objects.
You’ll come away with a clear understanding of the Keypoint Skeleton tool, how it works, and how you can use it within your project to save time and bolster your overall annotation process.
In this Darwin Fundamentals session, we explore the Keypoint Skeleton feature, a particularly useful tool for 2D image and video annotation. In simple terms, Keypoint Skeletons are sets of predefined points, joints, and shapes that can be adjusted to match an object’s pose. They’re an efficient way to define object poses or create custom polygons for reuse in projects.
Eager to explore keypoint annotation tools and tricks in more detail? Explore our guide to keypoints and skeletons.
In this video, we start by demonstrating how to create a Keypoint Skeleton for a human hand, mapping each point and joint to the fingers. From here, we explain how to change the Instance Tracking ID of each point, to make use of the Keypoint Skeleton simple for your use case.
Next, we explore how to use the Keypoint Skeleton within your datasets once it's been set up. We showcase how to drag and drop the Keypoint Skeleton onto your frame, manipulate it to an object, and adapt it per frame. We also explain how the Keypoint Skeleton tool behaves in video, showcasing how the tool interpolates between varying frames so you only have to label a few frames to get a smooth transition that represents ground truth.
We also note one important thing: the Keypoint Skeleton is versatile, and not limited to specific object types. For example, it can be used to create custom polygons, such as cuboids or pentagons, to represent different objects.
You’ll come away with a clear understanding of the Keypoint Skeleton tool, how it works, and how you can use it within your project to save time and bolster your overall annotation process.
In this Darwin Fundamentals session, we explore the Keypoint Skeleton feature, a particularly useful tool for 2D image and video annotation. In simple terms, Keypoint Skeletons are sets of predefined points, joints, and shapes that can be adjusted to match an object’s pose. They’re an efficient way to define object poses or create custom polygons for reuse in projects.
Eager to explore keypoint annotation tools and tricks in more detail? Explore our guide to keypoints and skeletons.
In this video, we start by demonstrating how to create a Keypoint Skeleton for a human hand, mapping each point and joint to the fingers. From here, we explain how to change the Instance Tracking ID of each point, to make use of the Keypoint Skeleton simple for your use case.
Next, we explore how to use the Keypoint Skeleton within your datasets once it's been set up. We showcase how to drag and drop the Keypoint Skeleton onto your frame, manipulate it to an object, and adapt it per frame. We also explain how the Keypoint Skeleton tool behaves in video, showcasing how the tool interpolates between varying frames so you only have to label a few frames to get a smooth transition that represents ground truth.
We also note one important thing: the Keypoint Skeleton is versatile, and not limited to specific object types. For example, it can be used to create custom polygons, such as cuboids or pentagons, to represent different objects.
You’ll come away with a clear understanding of the Keypoint Skeleton tool, how it works, and how you can use it within your project to save time and bolster your overall annotation process.
Up next
3:49
Watch video

Auto-Annotate Tool
How does the Auto-Annotate tool work? We tackle accurate polygon and pixel-wise annotation masks.
3:49
Watch video

Auto-Annotate Tool
How does the Auto-Annotate tool work? We tackle accurate polygon and pixel-wise annotation masks.
3:49
Watch video

Auto-Annotate Tool
How does the Auto-Annotate tool work? We tackle accurate polygon and pixel-wise annotation masks.
16:35
Watch video
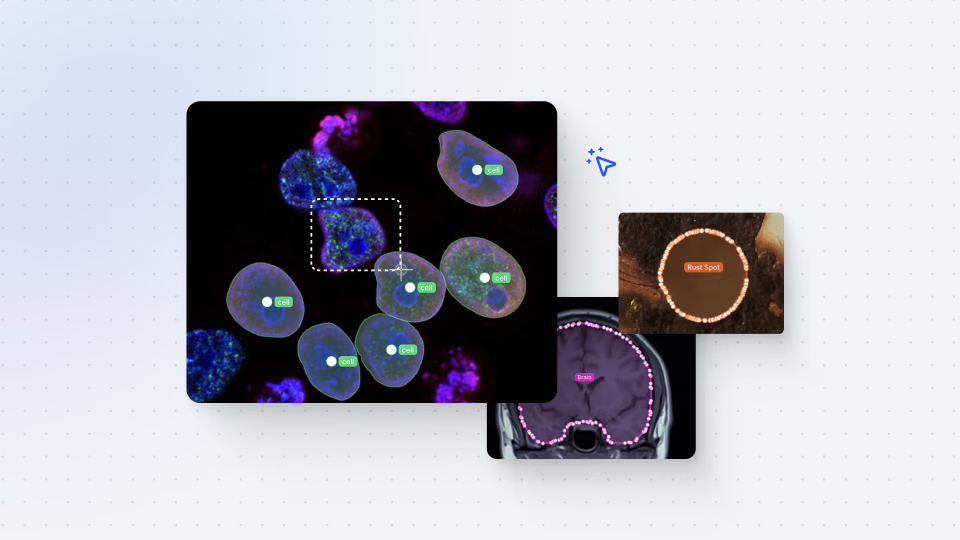
Annotations - Getting Started
We dive into image annotation and explain how you can get the most out of these impressive features.
16:35
Watch video

Annotations - Getting Started
We dive into image annotation and explain how you can get the most out of these impressive features.
16:35
Watch video

Annotations - Getting Started
We dive into image annotation and explain how you can get the most out of these impressive features.
5:56
Watch video

Auto-Annotate Tips & Tricks
Wield Auto-Annotate like the experts, with tips and tricks to accelerate your use of the tool.
5:56
Watch video

Auto-Annotate Tips & Tricks
Wield Auto-Annotate like the experts, with tips and tricks to accelerate your use of the tool.
5:56
Watch video

Auto-Annotate Tips & Tricks
Wield Auto-Annotate like the experts, with tips and tricks to accelerate your use of the tool.