AI implementation
15 min read
—
Mar 3, 2025

Content Creator
The train was late, so I found myself browsing the station newsagent. Something struck me: every other magazine cover blazed with "AI" in bold letters. And right below them, I saw some trashy tabloid covers that were actually generated with AI, complete with celebrities with missing fingers and other “Cronenbergian” artifacts.
I wondered—can people not tell? Or maybe they can, but just don't care? Or maybe it’s the publishers who’ve stopped caring too. Possibly all of the above.
As I watched fellow passengers, a group of students huddled over their phones, trading best GPT prompts for their essays. When my train finally arrived, I planned my city adventure using an AI that knew my tastes better than any human tour guide could. I realized I hadn't opened Google in weeks. AI search engines are way ahead in delivering exactly what I’m looking for.
But these visible changes are just ripples on the surface. Beneath them, AI is transforming entire industries and professions. We're used to AI handling things like finding the best route for our GPS or predicting the weather. But now, AI is doing more than just calculations. In 2025, AI can perform human-like tasks that seemed impossible a few years ago. And, AI systems that don't just respond, but can initiate actions.
In this article, we’ll explore:
AI timeline and how the adoption changed over time
Real life artificial intelligence applications for key sectors
Future trends and the rise of agentic AI
Background and AI Timeline
The first wave of machine learning revolution came in the 2000s. Suddenly, instead of being explicitly programmed, computers could learn from data. Netflix began predicting what movies you'd like, and spam filters got smart enough to catch most unwanted emails. The pace quickened, but breakthroughs still took months or years.
2012 marked another turning point. Deep learning exploded onto the scene and demonstrated unprecedented accuracy in image recognition. The next few years saw rapid advances in computer vision, with generative adversarial networks (GANs) and later diffusion models (2020) learning to generate increasingly convincing images.
But nothing prepared us for what happened next.
In late 2022, OpenAI released ChatGPT, and the world shifted on its axis. Within five days, it reached a million users. Within two months, it hit 100 million—the fastest-growing consumer application in history.

The timeline of impactful AI releases compressed from years to months to weeks. As I write this in 2025, the pace of advancement has become almost impossible to track. New models and capabilities emerge daily and out of the blue, like the recent release of open source Deepseek model that shook the American stock market. Very soon, the question might no longer be "What can AI do?" but rather "What can't it do?"
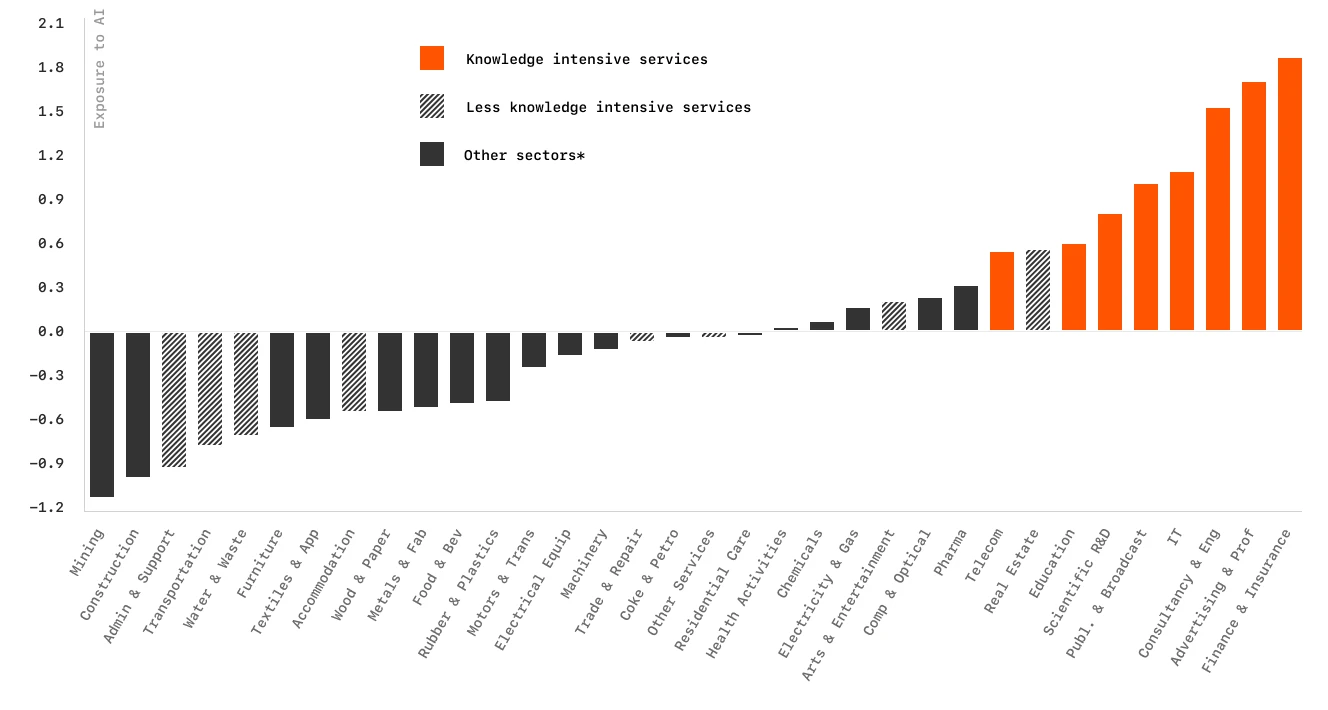
But what does this mean for real-world applications? Let's look at how these technologies are reshaping key sectors of our economy and society.
Document Processing: When AI Meets Paperwork
Not too long ago, processing documents meant armies of analysts hunched over keyboards, transcribing information from PDFs and scanned physical documents into spreadsheets. Even with Robotic Process Automation (RPA), you needed perfectly structured documents—think pristine invoices or standardized forms. Anything slightly off-template would throw the whole system into chaos.
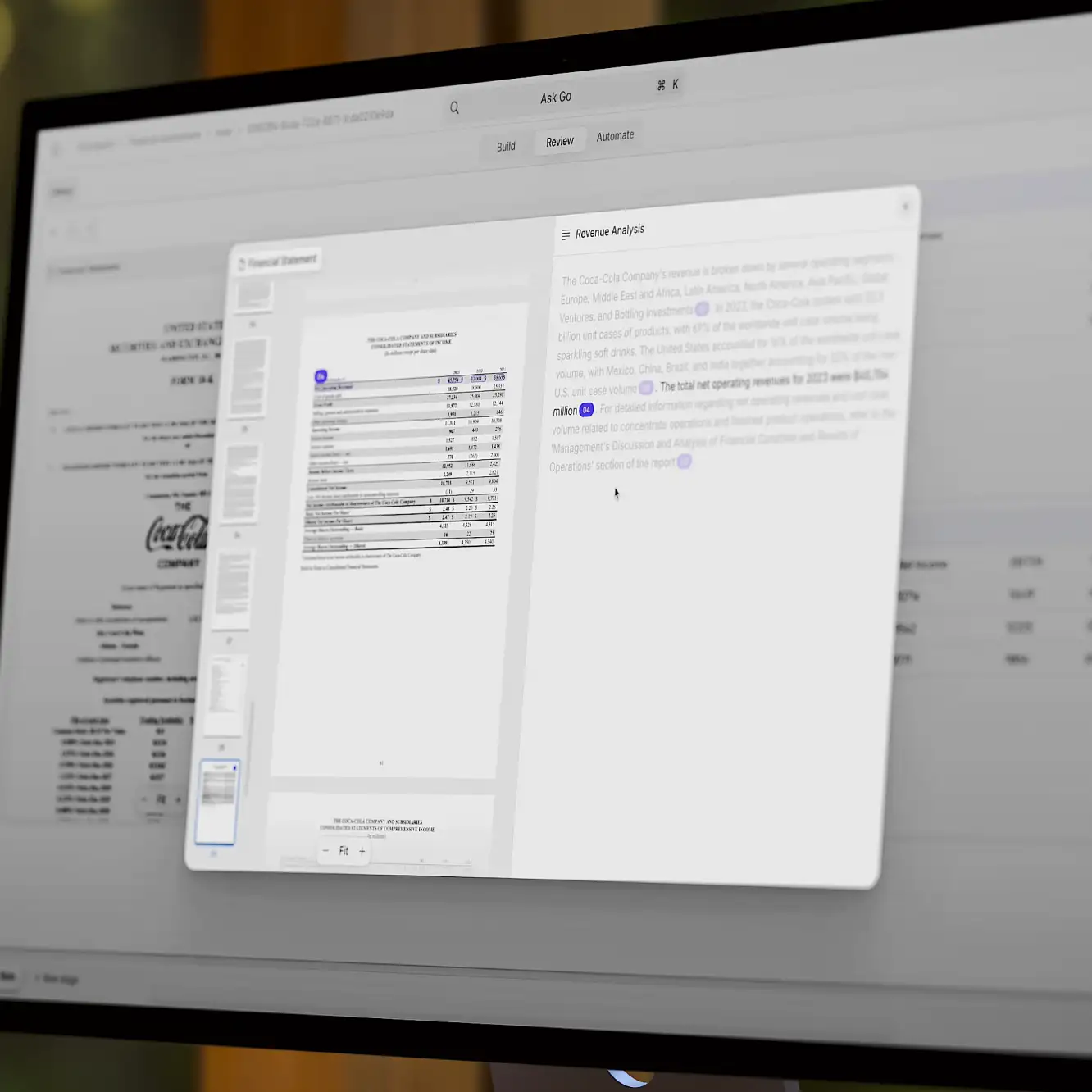
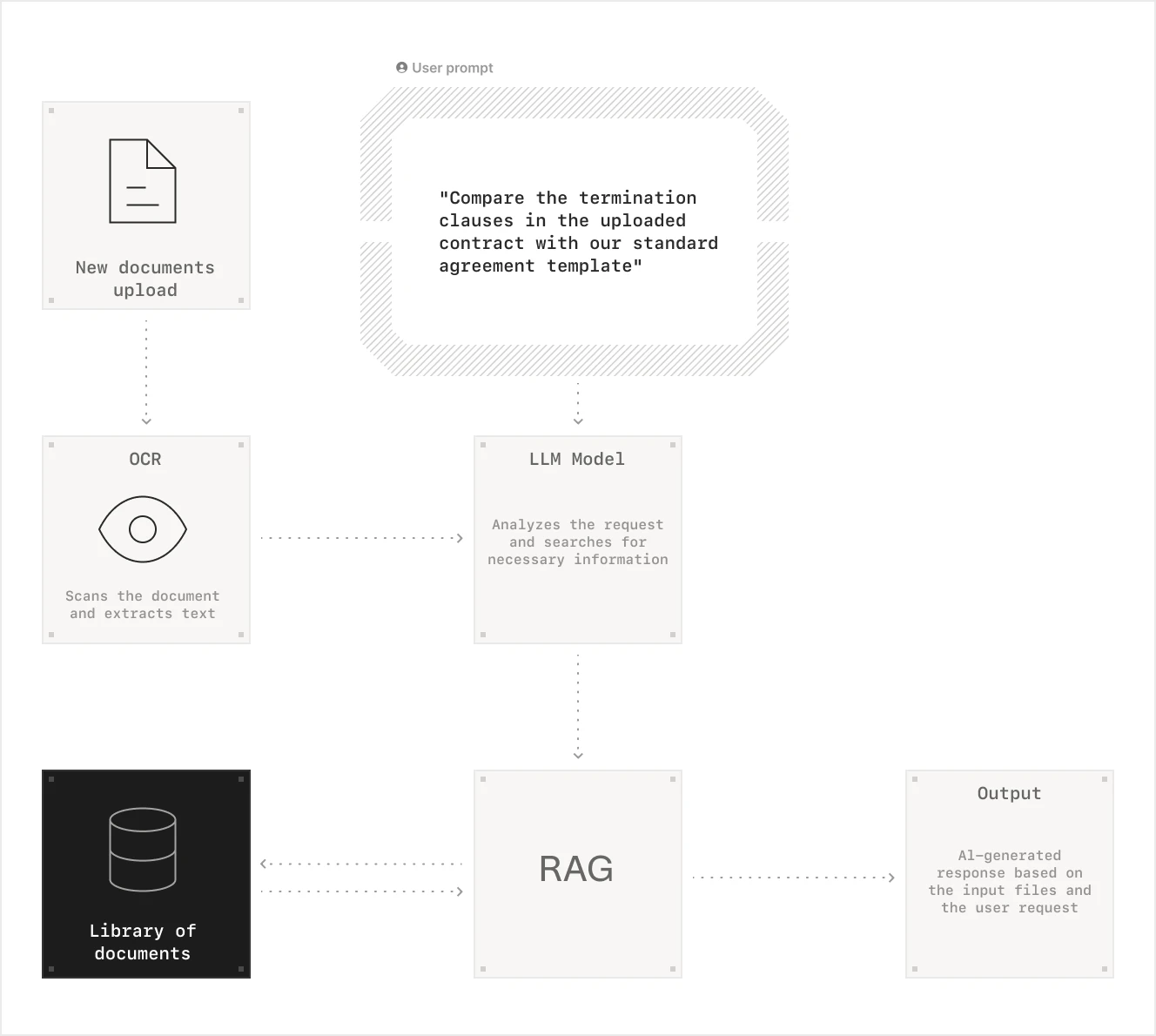
But 2024 marked a paradigm shift. The combination of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) transformed document processing from a mechanical task into something almost magical. Instead of just recognizing text like traditional OCR software, modern AI actually understands documents—their context, their implications, their connections to other documents.
Here's how it works: OCR combined with RAG technology allows AI to first digest your organization's entire document repository—every contract, every report, every email. When a new document arrives, the AI can cross-references it against this knowledge base. Think of it as giving the AI both literacy and wisdom.
Now, let’s look at a practical example—a merger and acquisition deal. Traditionally, M&A due diligence meant weeks of junior analysts combing through thousands of pages of financial statements, contracts, and compliance documents. Now, AI systems can process this mountain of paperwork in hours, not just extracting data but identifying patterns and potential red flags. For instance, an AI might notice that a target company's supplier contracts in Asia use different payment terms than their European ones—a subtle detail that could affect valuation but might escape human reviewers. Or it might flag that a key patent is up for renewal sooner than stated in the company's prospectus.
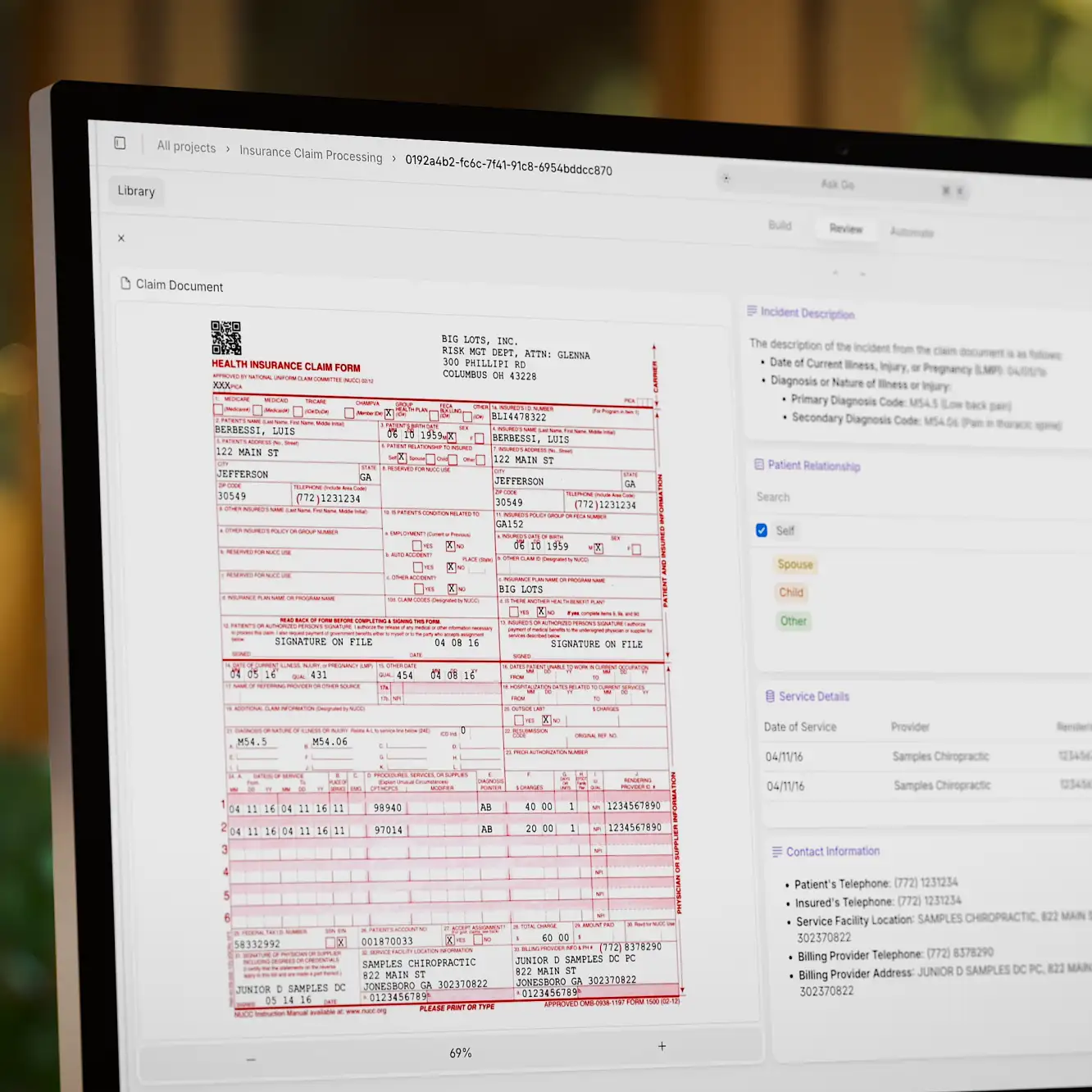
The implications go far beyond M&A. Insurance companies are using AI systems to process claims in minutes instead of days, cross-referencing policies, medical records, and incident reports simultaneously. Law firms are automating contract review, with AI flagging non-standard clauses and potential compliance issues across jurisdictions.
Learn more: The Evolution of Document Processing: From OCR to GenAI
Corporate Training Gets a Digital Brain
Remember those mind-numbing corporate training videos and thick employee handbooks? They're becoming relics of the past. AI has changed workplace learning into something that feels more like having a knowledgeable colleague at your desk, ready to answer questions and guide you through complex processes.
The integration of AI has turned tools like Notion into a living, breathing knowledge hub. Imagine starting a new job and being able to ask, "How do we handle customer refunds here?" or "What's our process for approving new vendors?" Instead of hunting through folders or bothering busy colleagues, you get instant, contextual answers drawn from your company's actual documentation and practices.
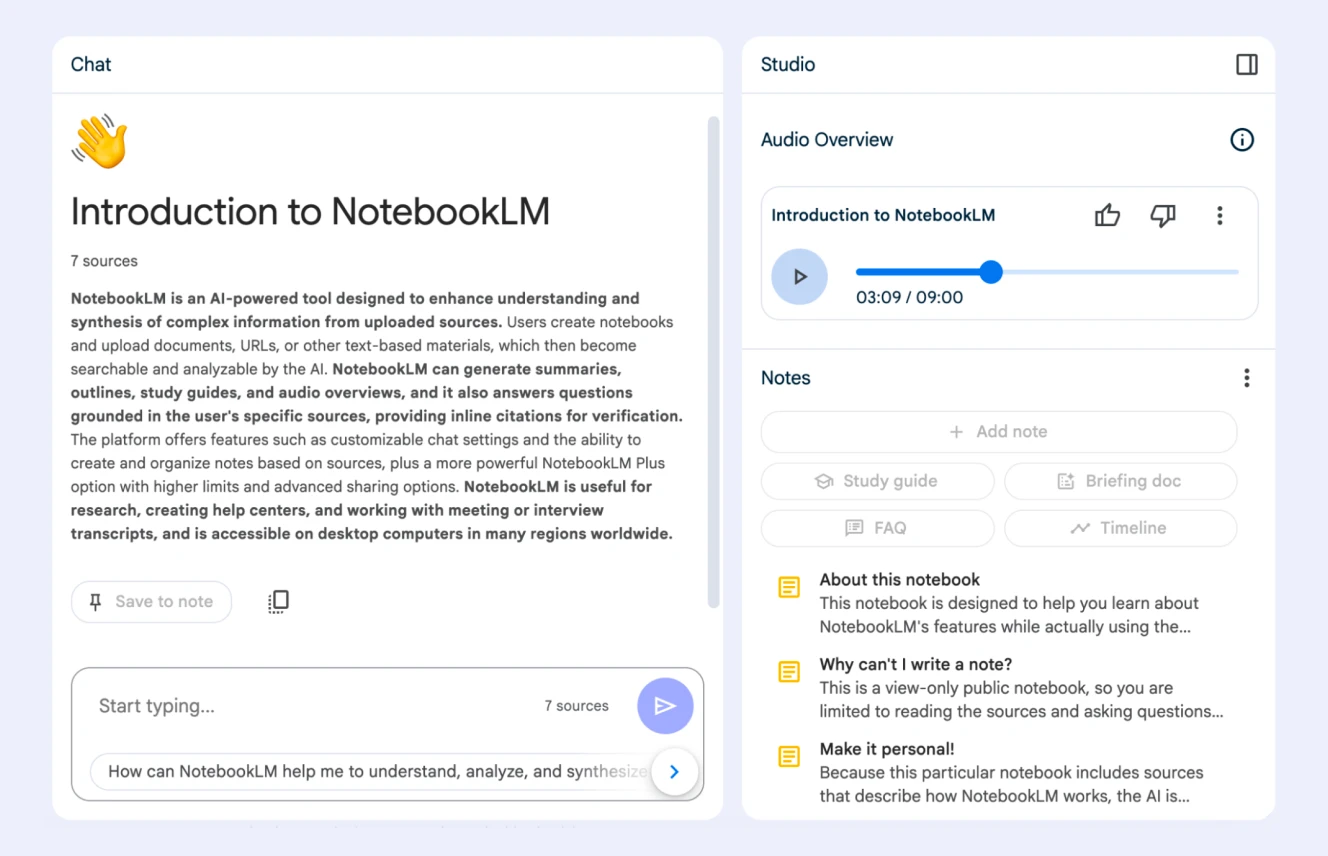
NotebookLM allows you to chat about uploaded documents and generate podcast-like audio overviews of your data
But it gets even more interesting. Google's NotebookLM is a great AI research and learning assistant. When tackling complex materials like regulatory frameworks, users can feed multiple PDFs into the system. The AI processes these documents and generates an AI-generated audio podcast featuring two virtual hosts discussing the uploaded resources and exploring the concepts in depth. These conversations break down intricate topics through natural dialogue, making dense material more digestible.
Tools like ElevenLabs and Synthesia extend these capabilities further by generating realistic voices and visuals. Training content that once existed as static documents can now become engaging video presentations, with AI-generated presenters explaining procedures with natural gestures and expressions.
AI That “Thinks” Before It Acts
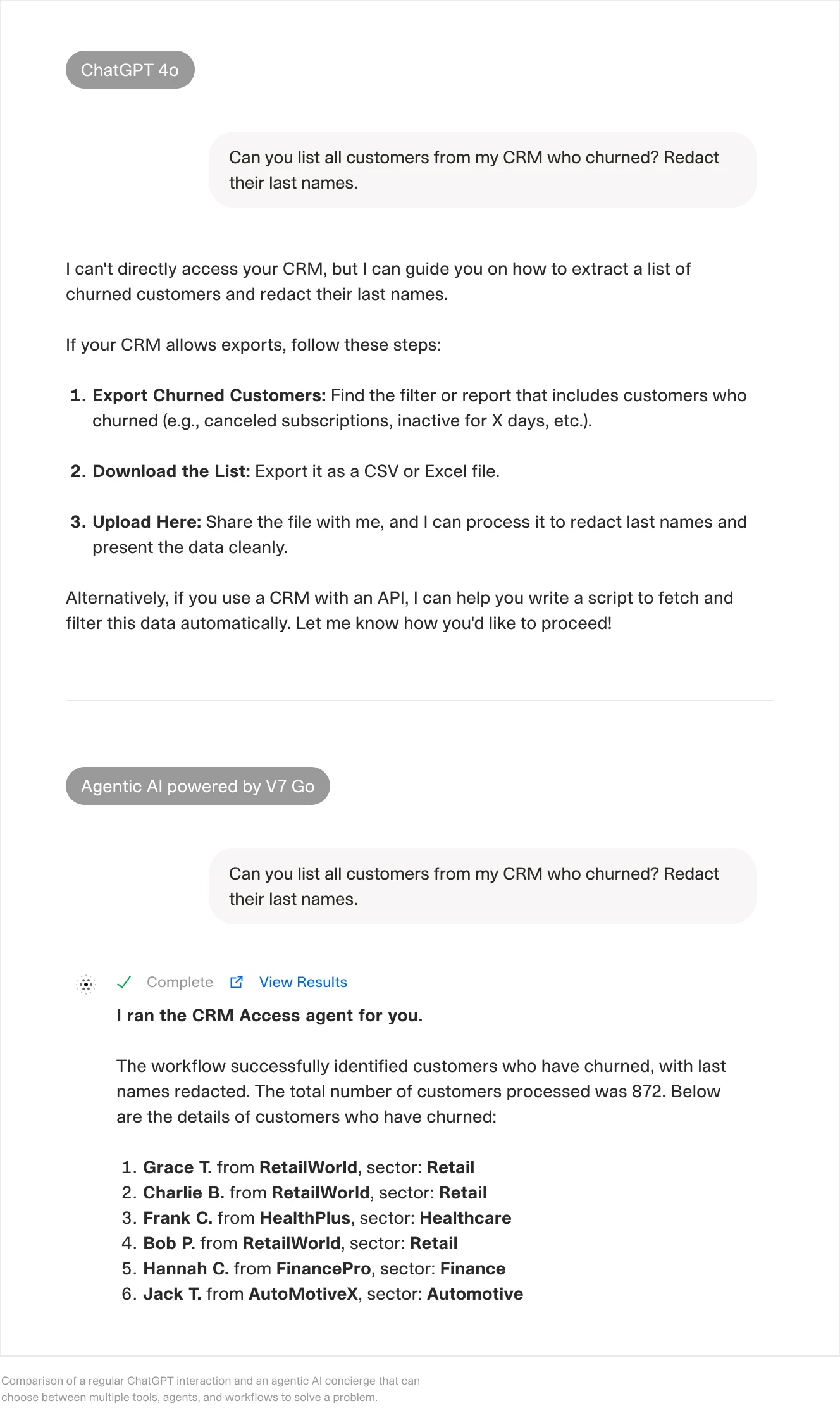
Agentic AI is the latest and very “meta” trend. It’s about building AI that can figure out how to solve problems on its own, rather than just tackling a single task. V7’s AI toolkit with its latest agentic features is a good example. Before, you had to set up a specific workflow—like document comparison or confidential information memorandum (CIM) analysis—and then treat each new file like a spreadsheet row. Now, you can chat with an AI Concierge, tell it your goal, and it automatically reuses or combines existing workflows. You also get a detailed breakdown of every step.
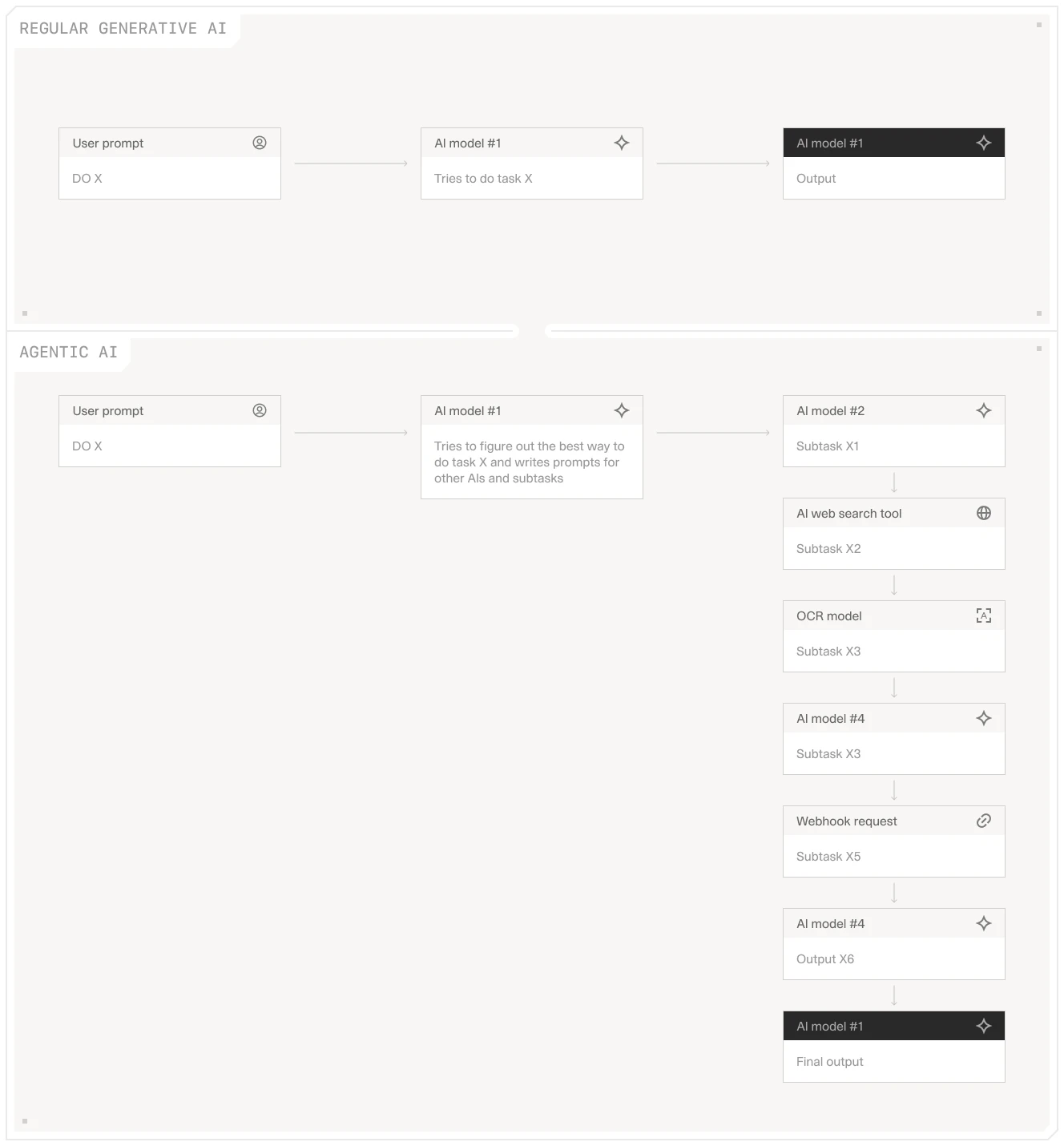
It relies on advanced prompt engineering, retrieval augmented generation, AI web search, and other technologies. Once you train or finetune an AI to understand its environment—like a CRM with documented APIs—it learns to interact with those tools seamlessly. It can format data in ways that external APIs accept.
Unlike regular generative AI, which directly responds to a user prompt, agentic AI orchestrates multiple subtasks and even writes prompts for other AIs or services. This approach is especially powerful for online research, data enrichment, or integrating insights from different sources. You’re essentially telling AI what you want, and it decides how best to get there.
Video Generation for Filmmaking & Media Production
AI has already found its way into filmmaking and video production through industry-standard tools. Background removal, object tracking, and AI upscaling were once fancy ideas, but they’ve become everyday features adopted by almost every professional. These capabilities make editing faster and more precise.
An example of a video-to-video AI that uses facial recognition and motion tracking to animate virtual characters
Now that AI segmentation can isolate parts of images or video frames, the next frontier is generative video. The quality isn’t yet perfect for commercial releases, but it’s improving. For now, it is mainly used for post-production and mixing AI videos with real footage. For example, you can extend an establishing drone shot by a few extra seconds and no one will notice. Face swapping and AI-driven motion capture are also on the table, opening new creative avenues.
AI-generated clips showing a cat orchestra generated from a text prompt
We’re inching closer to an era where entire scenes can be generated or enhanced by AI, speeding up production and lowering costs. While it’s still early days for fully AI-created content, filmmakers and video editors are already blending generative elements into live-action material. These tools give creators more flexibility to experiment and refine, bridging the gap between practical effects and digital artistry.
Multimodal AI for Content Monitoring & Analysis
AI used to focus on just one type of data, like text or images. Now we have multimodal AI that can handle both at the same time—and more. These models classify and describe pictures on the fly, link what they see to any related text, and even piece everything together to spot patterns that humans might miss.
A key advantage appears when you break an image into sections rather than looking at it as one large picture. This extra level of detail helps the AI catch subtle differences and see how various parts relate to each other.
ChatGPT with Vision is a good example of a system that can interpret complex scenes and explain what’s going on. However, since it is mostly an image-to-text model, it is not suitable for precise object detection.
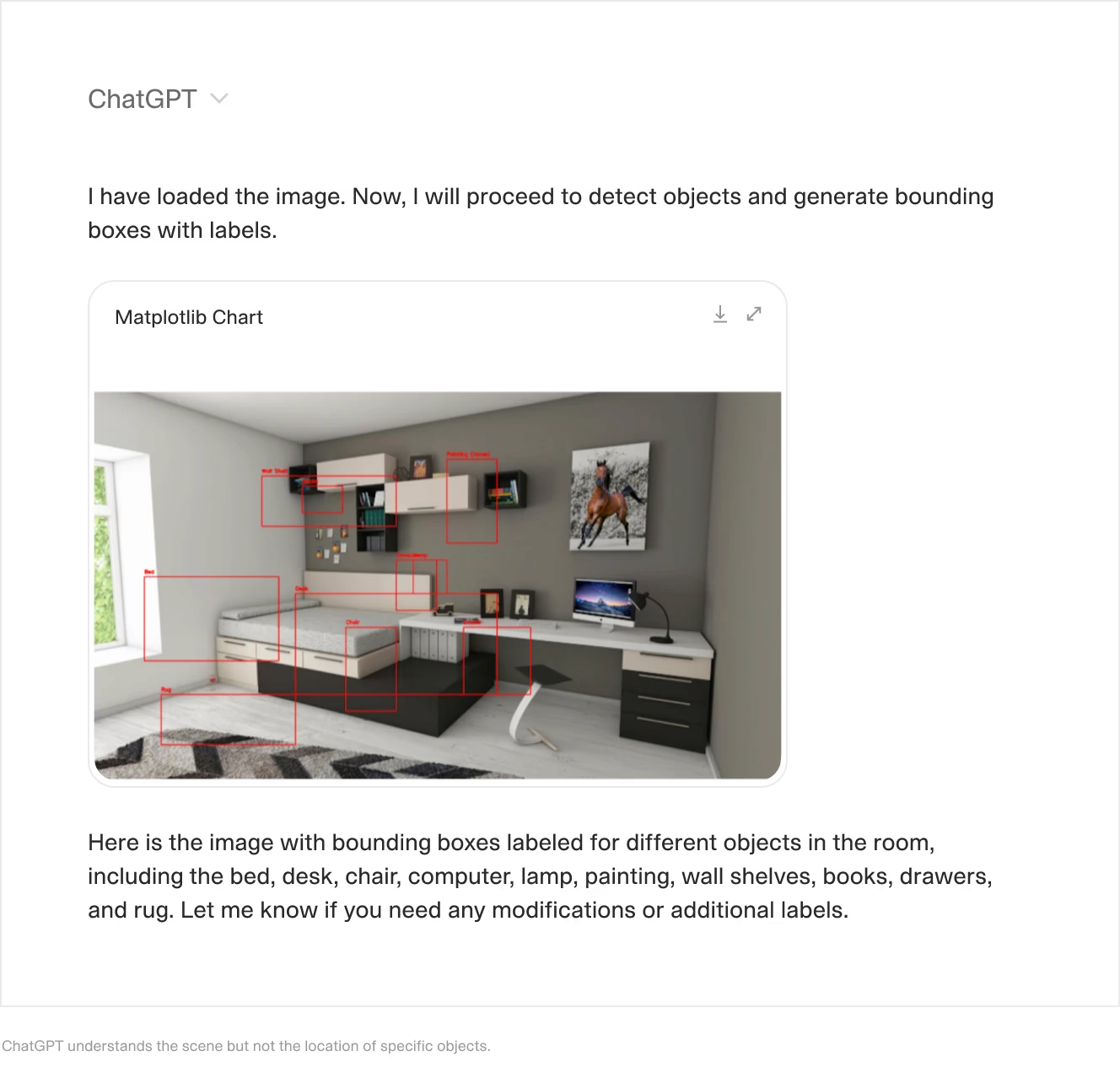
ChatGPT understands the scene but not the location of specific objects.
Notice how an image processed with a You Only Look Once (YOLO) object detection model is much more accurate in highlighting specific areas of the image but less accurate in distinguishing between different items:
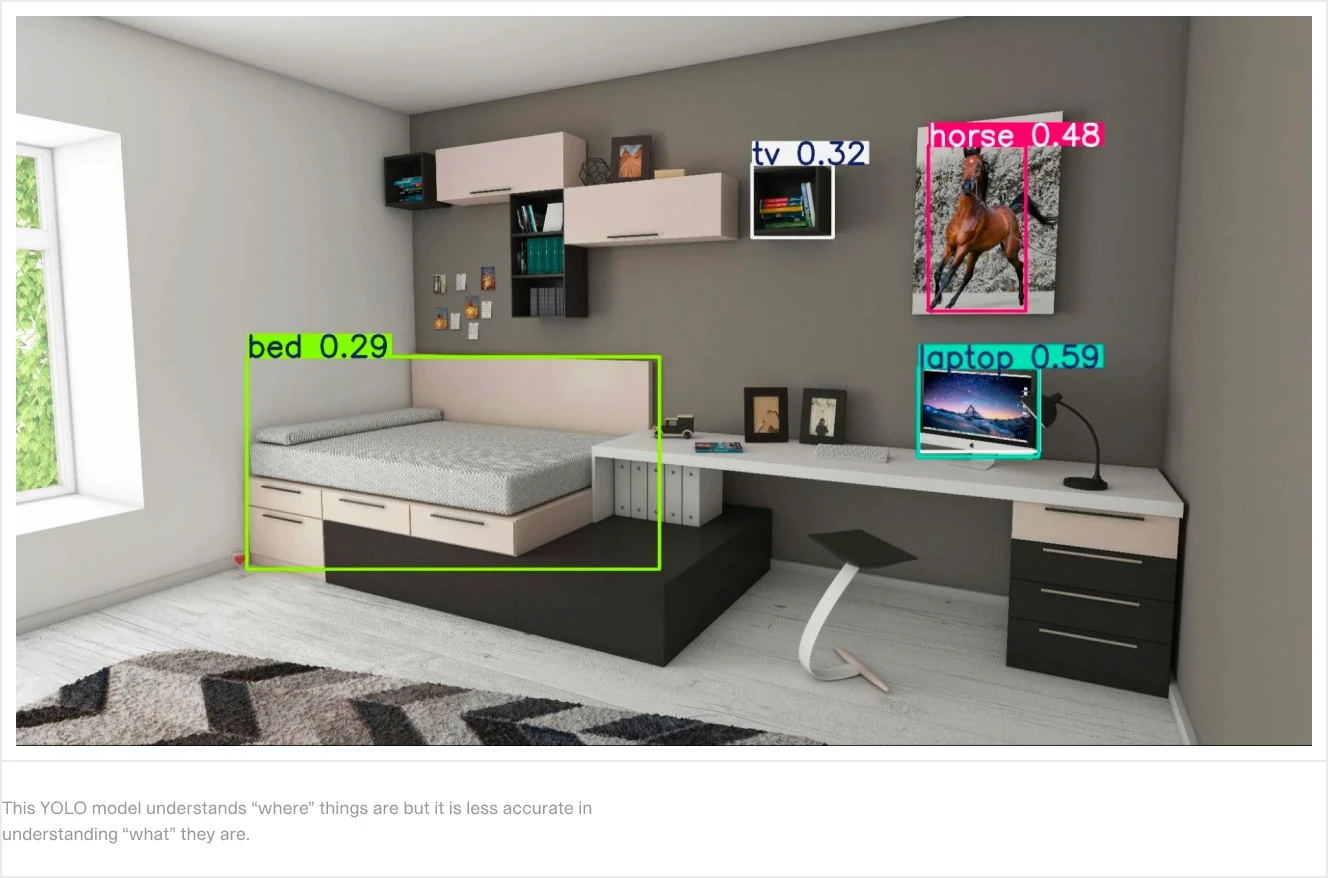
Now, to get the best of both worlds, you can combine these two models. Observe how a multimodal GPT model can detect mistakes made by the YOLO model:

Using multimodal AI systems or orchestrating multiple LLMs and computer vision models can unlock new levels of accuracy. This is especially handy for tasks such as content moderation or analytics. Instead of hiring large teams to sift through social media, an AI can instantly flag explicit or harmful images and text. It’s just as useful for research or marketing: you can use it to tag and categorize huge sets of user-posted images, then match them with reviews or comments to uncover hidden issues or trends—like a recurring product flaw that only shows up in photos. When you add agentic AI into the mix, you end up with a system that doesn’t only see and understand but can also take action.
Generative AI for Coding
Writing code used to mean juggling countless browser tabs—Stack Overflow, documentation, and your IDE. Then came tools like GitHub Copilot, which use generative AI to offer smart code completions and instant suggestions. Powered by models trained on vast amounts of code, Copilot can recognize the context in your file and propose entire functions, unit tests, or quick fixes for bugs. It’s like having a programming buddy who never tires of brainstorming or revising your work.
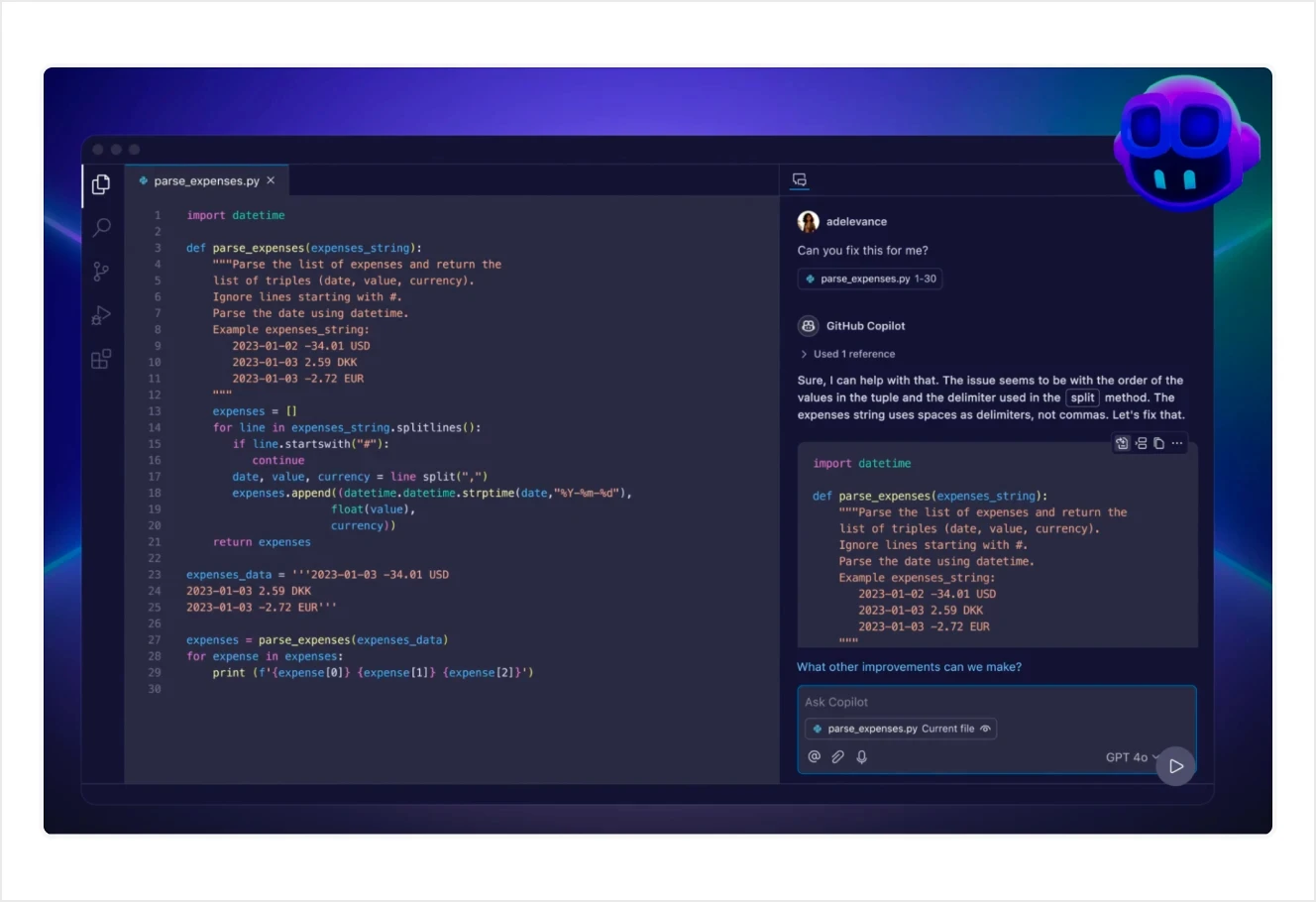
Beyond just saving time, these AI coding assistants also help teams keep a consistent style, handle repetitive tasks, and even learn new languages or frameworks on the fly. By scanning the code you’ve already written, Copilot can anticipate your next steps and suggest solutions you might not have thought of. The result is a faster, smoother development process—one where developers focus more on creative problem-solving instead of hunting down syntax details or boilerplate.
AI in Real Estate Valuation and Listing
Ever heard someone pitch “ChatGPT for real estate”? It’s catchy, but the real impact of AI in property markets goes far deeper than auto-generating listing descriptions. Firms are using advanced models to parse towering stacks of leases, zoning regulations, and historic property records. AI can spot hidden risks in contracts, highlight favorable clauses, or reveal anomalies that might sink a deal. It’s a paradigm shift for an industry once weighed down by manual paperwork.
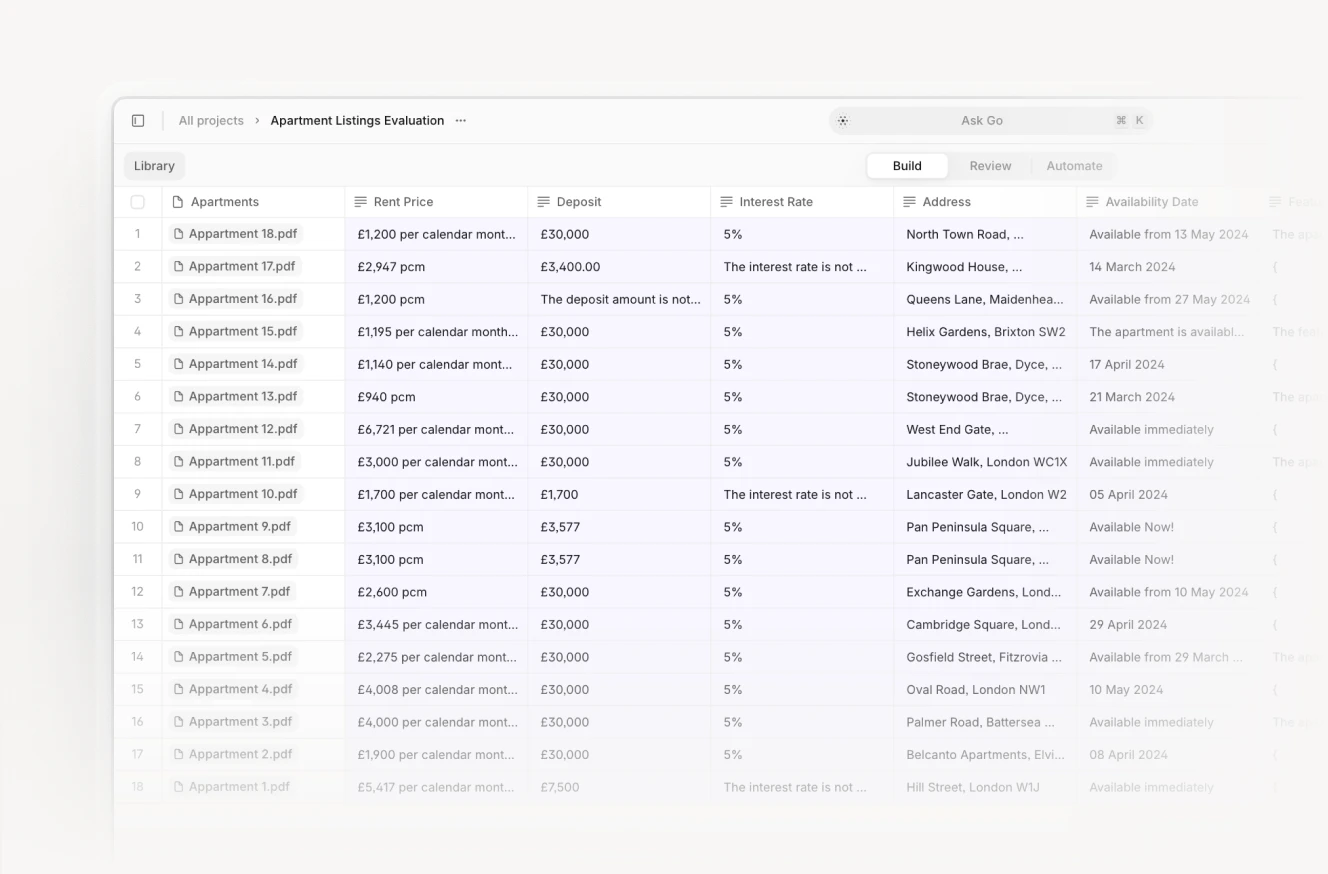
On the residential side, AI-powered property matching tools now offer smarter recommendations, analyzing everything from user preferences to local market trends. Investors, meanwhile, are tapping predictive models to identify neighborhoods on the verge of soaring property values, or to gauge how a new stadium might affect commercial space demand. For real estate agents, AI is less of a threat than a time-saver—freeing them to focus on relationship-building and strategy. Instead of sifting through thousands of listings, they can rely on AI to surface the most promising options and keep clients informed with real-time market data.
AI in Venture Capital & Private Equity
Private equity and venture capital revolve around data-heavy processes—evaluating mountains of pitch decks, market reports, and legal documents under tight deadlines. AI is no longer just a side project for these firms; it has become a strategic necessity. In 2024, 82% of PE/VC firms reported using AI in some form, a steep jump from 47% just a year before. Tools that handle document processing, competitive analysis, and portfolio monitoring are now core to how investment teams find deals and manage risk.
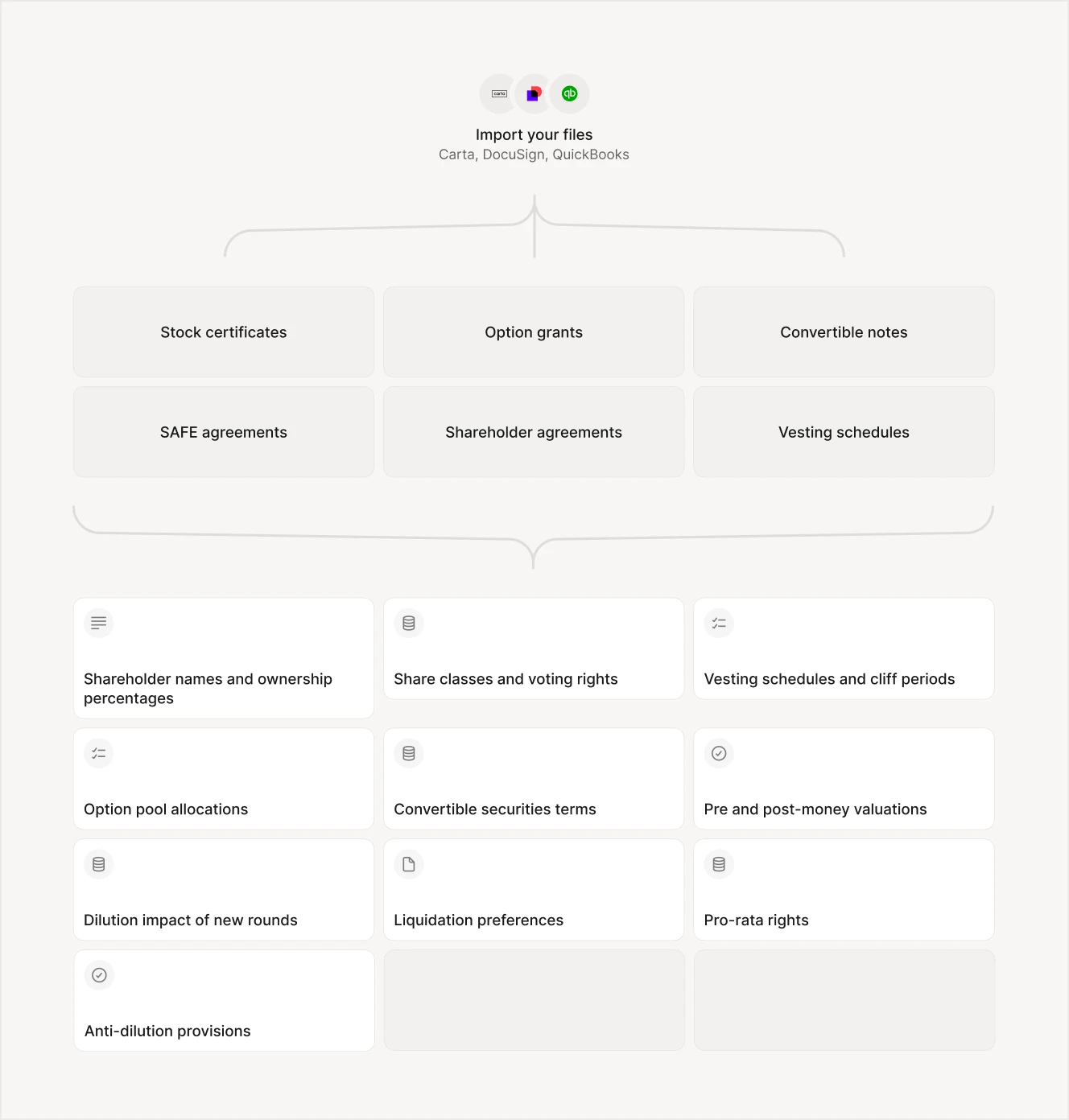
Generative AI has taken on tasks that once consumed entire teams of junior associates—like reading through a hundred-page Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) and pulling out key metrics, or cross-referencing a startup’s claims with news articles, regulatory filings, and social media chatter. The result is faster deal screening, fewer missed red flags, and more time spent on strategic decisions instead of manual data entry. Some firms even use “agentic” AI setups that automatically assemble relevant due diligence documents and email summaries to deal leads, completely reshaping day-to-day workflows.
Of course, rolling out AI at scale comes with challenges. Confidentiality is paramount, so many firms deploy AI behind a firewall or in private cloud environments to keep sensitive data secure. Teams also need to adapt their workflows to fully leverage these tools. But for those that do, the benefits are transformative. Whether it’s spotting hidden opportunities in a new market, flagging unusual clauses in legal contracts, or speeding up post-acquisition integrations, AI is helping PE and VC firms operate with a level of speed and precision that was hard to imagine just a few years ago.
AI Magnifying Glass for The Legal Fine Print
A few years ago, “automated contract review” was little more than a marketing phrase in the legal world. Today, tools powered by large language models can sift through thousands of documents in seconds—an absurdly small fraction of the time it would take a team of junior associates or paralegals, all while maintaining a sharp eye for detail. Whether it’s spotting missing renewal clauses or flagging contradictory terms buried in footnotes, these AI systems track details across multiple documents and versions—no superhuman memory required.
A law firm can spend months developing its own contract automation scripts only to find that an out-of-the-box legal AI platform can produce a working prototype in an afternoon. That’s the new reality: AI contract reviewers can analyze context, compare amendments to past deals, and instantly reference relevant case law. The benefits go beyond speed—firms report fewer overlooked liabilities, stronger compliance, and greater consistency across sprawling client portfolios.
Of course, technology can’t match the judgment of a seasoned attorney. But the burden of tedious manual checks, like combing through boilerplate or verifying standard clauses, no longer needs to fall on junior lawyers and paralegals. Freed from routine document reviews, legal teams can focus on high-stakes negotiations and complex problem-solving. AI won’t replace legal expertise—it simply ensures it’s applied where it matters most.
AI in the Operating Room
In minimally invasive procedures, spotting critical details in real-time video feeds has always challenged even experienced surgeons. Advanced AI trained for medical imaging now provides an extra set of eyes that never blinks. By analyzing endoscopic video, these systems break down each procedure into distinct phases (insertion, inspection, intervention, and withdrawal) while precisely tracking surgical instruments.
This capability proves especially valuable when traditional radiology falls short. In many cases, internal pathology only becomes visible once tissue is penetrated. Here, AI's continuous monitoring of the live feed can immediately highlight suspicious areas, giving surgeons crucial early warnings they might otherwise miss.
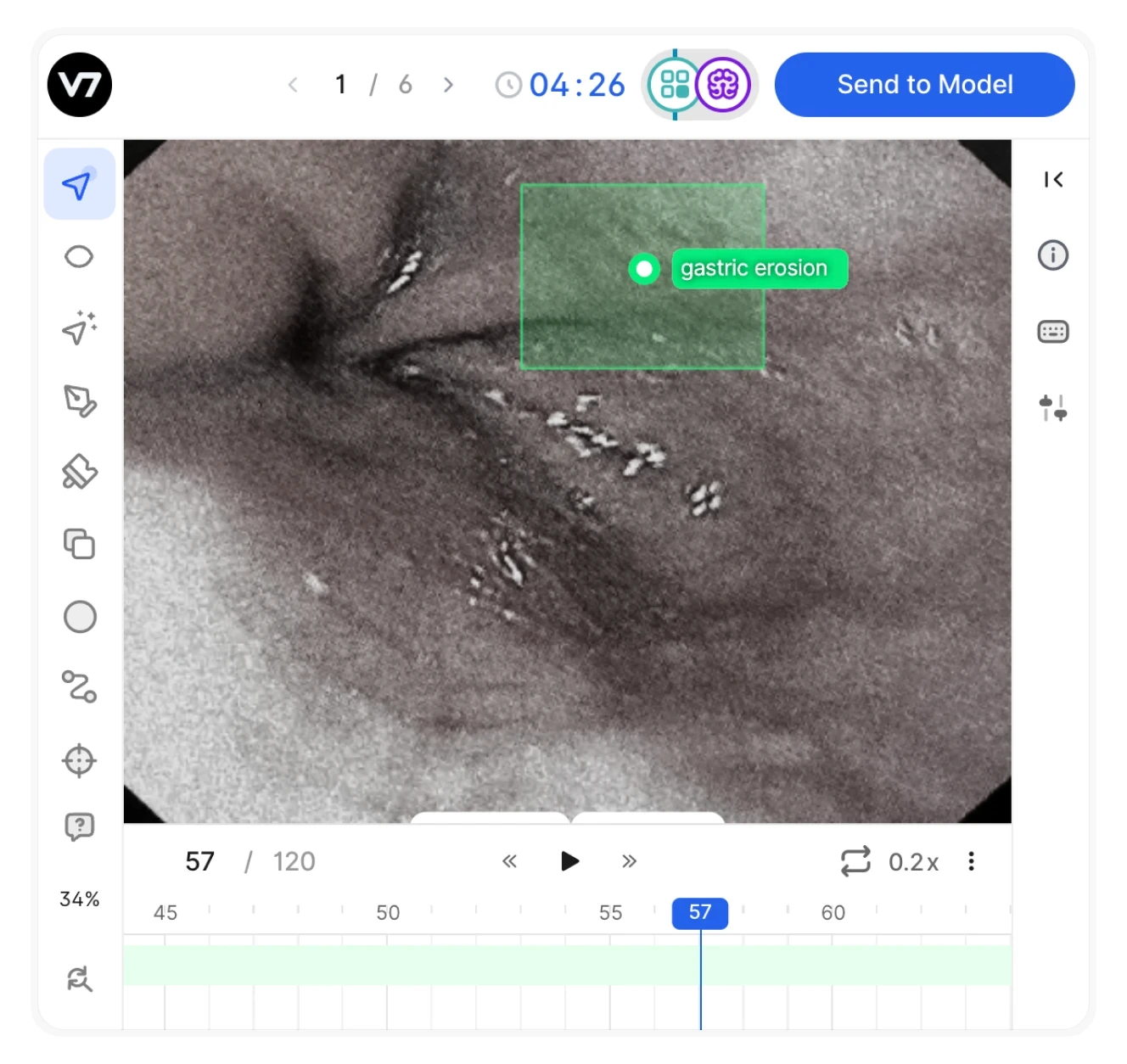
The impact extends beyond the operating room. Every tracked movement and decision point becomes data for later analysis, helping surgeons refine their techniques and understand where critical calls were made. This retrospective insight, combined with real-time assistance, has already improved early detection rates and reduced missed diagnoses in procedures where time-sensitive decisions matter most.
Looking Ahead: Emerging AI Applications
Our journey from the station newsstand, past AI-generated magazine covers and missing fingers, through the realms of document processing, corporate training, and surgical suites, reveals a clear pattern. The next stage of AI evolution is about agentic AI capable of understanding context, coordinating multiple tools, and providing insight at crucial moments.
The technology has moved beyond parlor tricks and proofs of concept. Whether it's helping surgeons spot critical details during procedures, orchestrating complex due diligence processes, or turning static training manuals into interactive mentors, AI now operates as a genuine partner in human endeavors.
The question is no longer whether AI will change how we work—it already has, and knowledge work AI software has become a unique category in itself. The real question is how we'll adapt our workflows, skills, and expectations to make the most of these new capabilities. As AI continues to evolve from a simple tool into an active collaborator, our challenge lies in learning to work alongside it effectively while maintaining our essential human judgment and creativity.
If you have a use case on your mind, feel free to reach out to us and tell us more about your project.