Knowledge work automation
27 min read
—
Feb 12, 2025

Content Creator
Artificial intelligence (AI) projects often start with grand ambitions, yet many never make it past the planning stage. According to a recent study, 11% of U.K. businesses have at least 50 stalled AI projects. Even well-funded initiatives often struggle to reach production. The reasons vary—data quality issues, integration challenges, and misalignment between business needs and technical execution.
Stories like this are common—ambitious AI projects that miss the mark due to misaligned goals or unforeseen complexity. McKinsey’s analysis of enterprise AI initiatives highlights a key insight for successful implementation: start by defining the problem in clear business terms, then evaluate whether existing technologies can address the need.
That said, some use cases naturally lend themselves to repeatability and reliability, making AI particularly well-suited to address them. This article cuts through common misconceptions to examine where AI truly delivers business value.
We’ll explore:
Strategic frameworks for evaluating AI necessity and applicability
Evidence-based examination of successful AI implementations
Practical approaches to risk mitigation and value creation
Real-world case studies of both successes and failures
The following sections provide decision-makers with actionable insights drawn from documented implementations across industries. Rather than chasing technological capabilities, we emphasize a pragmatic approach and focus on business outcomes—examining how organizations have effectively integrated AI to address specific operational challenges.
Our analysis starts by examining AI's role in modern business operations, with a focus on generative AI solutions like large language models (LLMs) and other foundation models. Rather than promoting AI adoption for the sake of “innovation,” our goal is to provide a clear, objective perspective on where and how AI can truly improve business performance.
Impact of AI on Business
Let’s start with a candid look at AI’s impact on business operations—the successes, the struggles, and the lessons learned that often go unreported. Is AI adoption happening too early? How soon is too soon? Does your company even need AI right now? And how effective has AI been for companies piloting its implementation?
The timing of AI adoption poses a critical challenge for businesses today. Many organizations learn this the hard way. The pattern is all too familiar—months spent developing AI models or finetuning LLMs, only to discover that the latest iteration of ChatGPT or an off-the-shelf alternative surpasses their solution across every benchmark. Bloomberg’s case has become a prominent example of this scenario:

Solutions often risk becoming obsolete before they even reach deployment. Just as one technology is implemented, a disruptive breakthrough emerges, perfectly matching the intended use case. Even frontier models from industry leaders like OpenAI face growing competition from open-source alternatives. For instance, Meta's LLaMA models offer high-quality, freely available large language models that companies can fine-tune for specialized applications. Similarly, the Chinese startup DeepSeek has developed the DeepSeek-R1 model, which rivals leading proprietary models in performance while being more cost-effective.
On the flip side, the opposite problem frequently arises—a new flashy AI tool often turns into a solution in search of a problem, rather than addressing genuine business needs. AI adoption still presents a significant challenge for organizations, with 74% of companies struggling to achieve and scale measurable value from their initiatives. While AI continues to dominate discussions around innovation, many businesses face hurdles such as unclear objectives, poor integration, and difficulties transitioning from proof-of-concept to production.
The special case of AI copilots in knowledge work automation
However, the picture isn’t entirely bleak. Many organizations are realizing significant operational gains as professionals enhance their productivity through targeted automation of routine tasks. Adoption driven by individual teams or employees championing AI within their organizations often proves more commonplace than some top-down initiatives. AI also demonstrates strong effectiveness in AI assistant or copilot applications, offering valuable support in augmenting human capabilities. This highlights an important insight—AI won’t replace entire professions, but professionals who use AI effectively will outpace and replace those who don’t.
The competitive landscape adds urgency to this dynamic. If you wait until your specific problem has a polished, easy-to-implement AI solution, it will likely have become the industry standard rather than a competitive advantage. Success often requires getting your hands dirty and iterating on challenges, accepting small efficiency gains while building toward better performance over time.
So, where does AI bring the most value, and in which scenarios is it still very much in an experimental phase?
Business Applications of Artificial Intelligence
The Good, the Bad and the Ugly
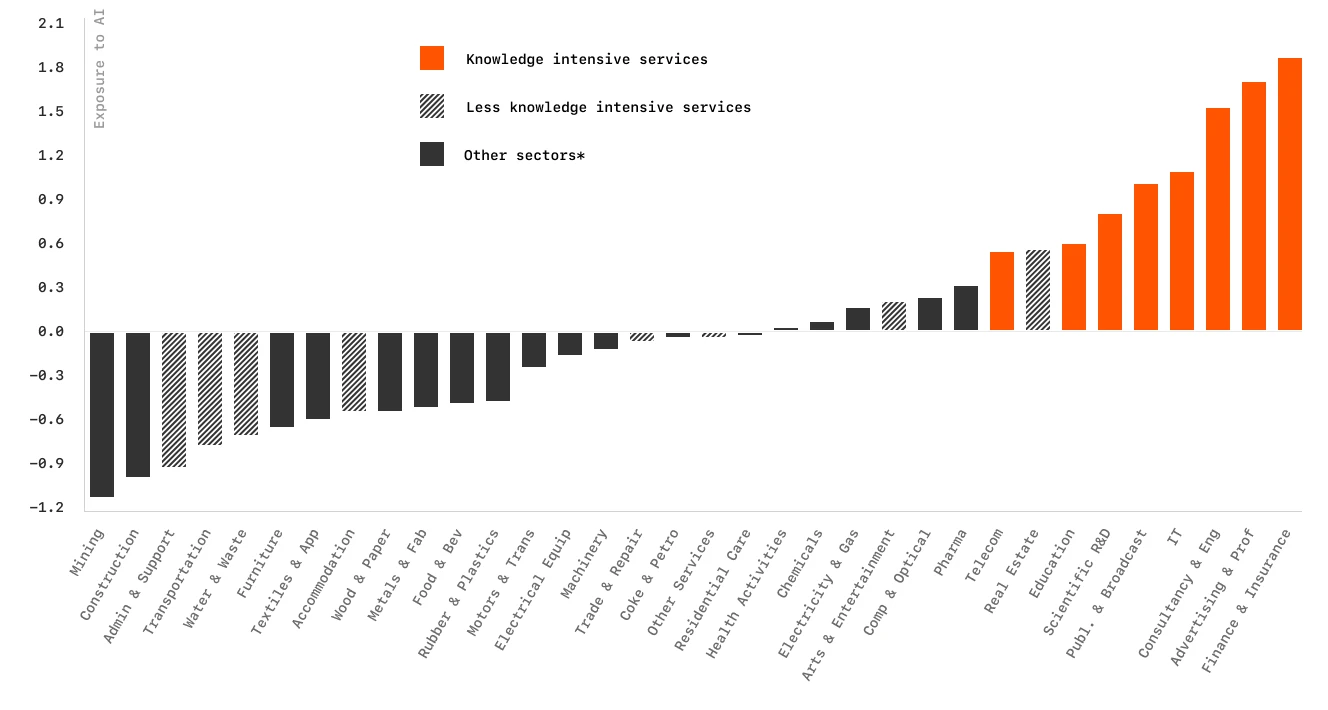
In many ways, AI—and especially generative AI like ChatGPT—has become a sort of modern-day snake oil, marketed as a solution to far too many problems. In many cases, companies try to sell AI products built on prompt engineering rather than meaningful advancements that enhance model performance. As a result, many use cases that these platforms claim to address ultimately fall short of expectations.
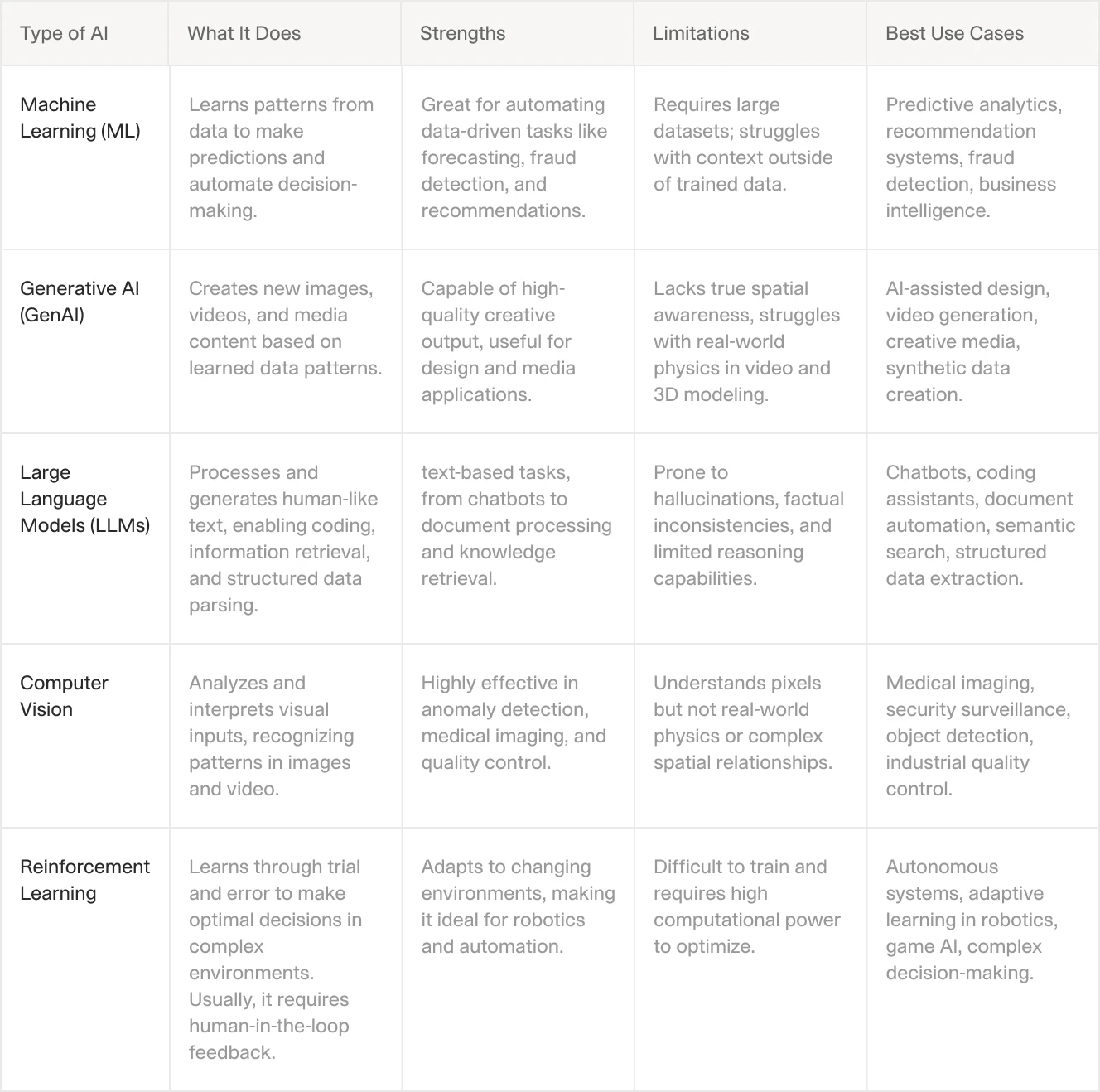
Let's be clear about what AI can and can't do. Instead of vague promises, here's what actually works and what doesn't. The hierarchy is quite clear—AI is good at data processing and pattern recognition but struggles with tasks requiring nuanced understanding or creativity.
Things AI Does Well
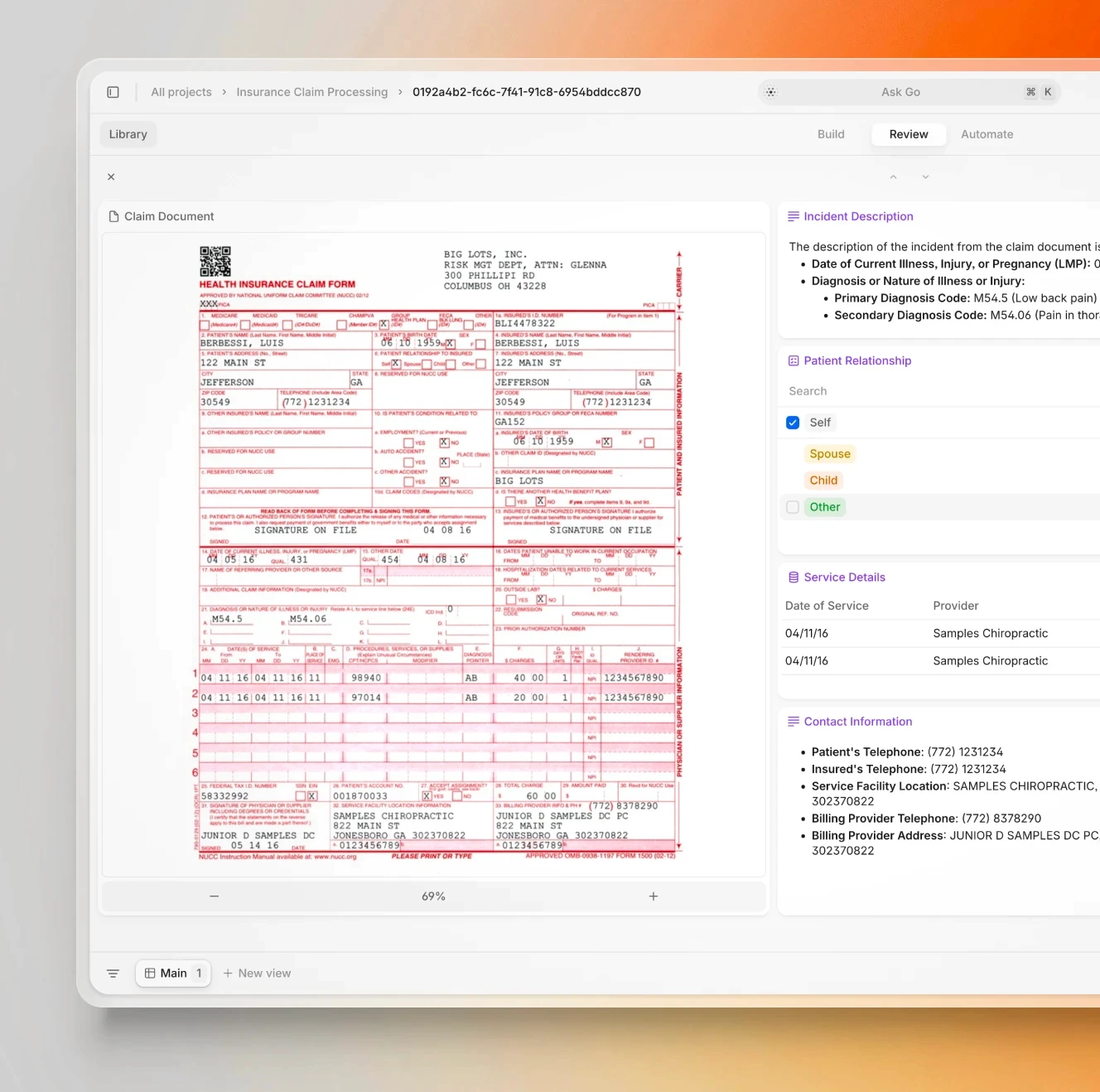
Extracting information from PDFs and other files and converting it into structured outputs is one of the most promising large-scale applications of AI and language models.
Data Handling
Data extraction • Data parsing • Unstructured data processing • OCR • Document understanding
AI is very good at handling the "boring" and "tedious" tasks—extracting data from documents, analyzing large volumes of text, and parsing information. It’s like having a tireless assistant that never gets bored of paperwork. Historically, businesses have struggled with back-office tasks involving extensive manual data entry, navigating between systems or spreadsheets, and moving information from one place to another. Modern AI for document processing has effectively solved these challenges.
Spotting Problems
Medical imaging segmentation • Object detection • Human activity recognition • Anomaly detection • Quality control vision systems
AI can find a tiny abnormality in a medical scan, spot someone not wearing safety gear in a warehouse, or identify defective products on a production line. If something looks wrong, AI can usually flag it—and these catches often save companies from costly problems.
Making Connections
Vector embeddings • Semantic search • Knowledge graphs • Neural information retrieval • Recommendation systems
This one's interesting—AI can take massive amounts of data and understand how things relate to each other. Imagine reading thousands of research papers and instantly knowing which ones discuss similar ideas, even when the authors use completely different words. AI does this by turning information into what scientists call "latent space"—basically a giant map of how concepts connect. This approach powers many recommendation engines, like those used by streaming services. These systems can suggest videos, movies, or shows you might not even know you’d enjoy, using subtle patterns and relationships within the data to make connections you wouldn’t have noticed yourself.
Number Crunching and Predictions
Predictive analytics • Time series forecasting • Sentiment analysis • Purchase intent classification • Business intelligence automation
Give AI your business data, and it will find patterns you might miss. It can analyze customer sentiment, predict buying behavior, and generate reports that actually make sense. This works particularly well when connected to existing business tools like CRMs and accounting systems.
AI Agents: Some frameworks can leverage multiple AI capabilities to perform a variety of tasks. Agentic AI solutions can decide how to solve a problem by dynamically combining different tools. Unlike traditional AI models that follow fixed scripts, AI agents adapt and select the best approach for each task. A financial analysis AI agent, for example, might use an LLM to extract key figures from statements, then select a risk analysis tool to calculate financial risks, and finally flag anomalies for human review.
Where AI Falls Short
State-of-the-art video generation AI models can create spectacular cinematic shots, but they often struggle with real-world physics. For example, notice how the steps of a stairway randomly split or how a small step propels a person six steps upward. These models lack a true understanding of perspective and spatial relationships—they simply generate visuals that appear "somewhat similar" to patterns in their training data.
Visual Arts and Videos
3D scene understanding • Physical interaction modeling • Motion synthesis • Temporal consistency • Design principles application
AI struggles with design and video. While it can create images, it doesn't understand basic design principles. Video is even worse—AI doesn't get how things work in three dimensions. That's why AI-generated videos look odd when people try to do simple things like eat, walk, or open doors. The AI still has no real understanding of how objects and people interact in the physical world.
Creative Work
Content generation • Narrative development • Brand voice adaptation • Creative writing
AI can write, but it can't write well. The output is usually generic and forgettable—fine for technical documentation or quick summaries, but not for anything requiring a genuine voice. It's like the difference between a form letter and a personal note. Ask AI to write an essay that avoids overused words like "fascinating" or "transforming," or to vary sentence lengths to mimic the rhythm of human conversation, and it will fall flat on its face.
Customer Service
Contextual understanding • Intent recognition • Omnichannel communication across multiple touchpoints
Anyone who's dealt with a chatbot knows this one. While AI can handle basic questions, it often fails at real customer service. A human saying "I don't know, but I'll find out" is far more reassuring than a chatbot repeating useless information. AI can support customer service, but it can't replace the human touch. Salesforce’s Agentforce is the latest attempt to push AI-driven customer service further, promising more autonomous, intelligent agents that can handle complex queries across multiple channels. However, even Salesforce faces challenges in making AI truly effective in customer interactions.
Complex Decisions
Multi-objective optimization • Ethical reasoning • Contextual decision-making • Ambiguity resolution
When situations get messy—unclear goals, competing priorities, ethical considerations—AI stumbles. It can't handle the nuanced judgment calls that humans make naturally. These situations require understanding context and making balanced decisions, something AI just isn't equipped to do.
Now that we understand these strengths and limitations, let’s explore how different industries are leveraging AI. This time, we’ll focus on sector-specific challenges where the technology delivers tangible benefits, such as reducing errors or improving efficiency.
Legal & Insurance Applications
Legal and insurance operations have always been document-intensive fields where attention to detail can make or break cases and claims. These industries were among the first to adopt AI, driven by the need to process vast amounts of textual information accurately and consistently. What used to take teams of paralegals and claims adjusters weeks to review can now be processed in hours.
Legal Document Review
Contract analysis • Clause extraction • Multi-document comparison • Legal precedent search • Citation verification • Risk assessment • Compliance checking
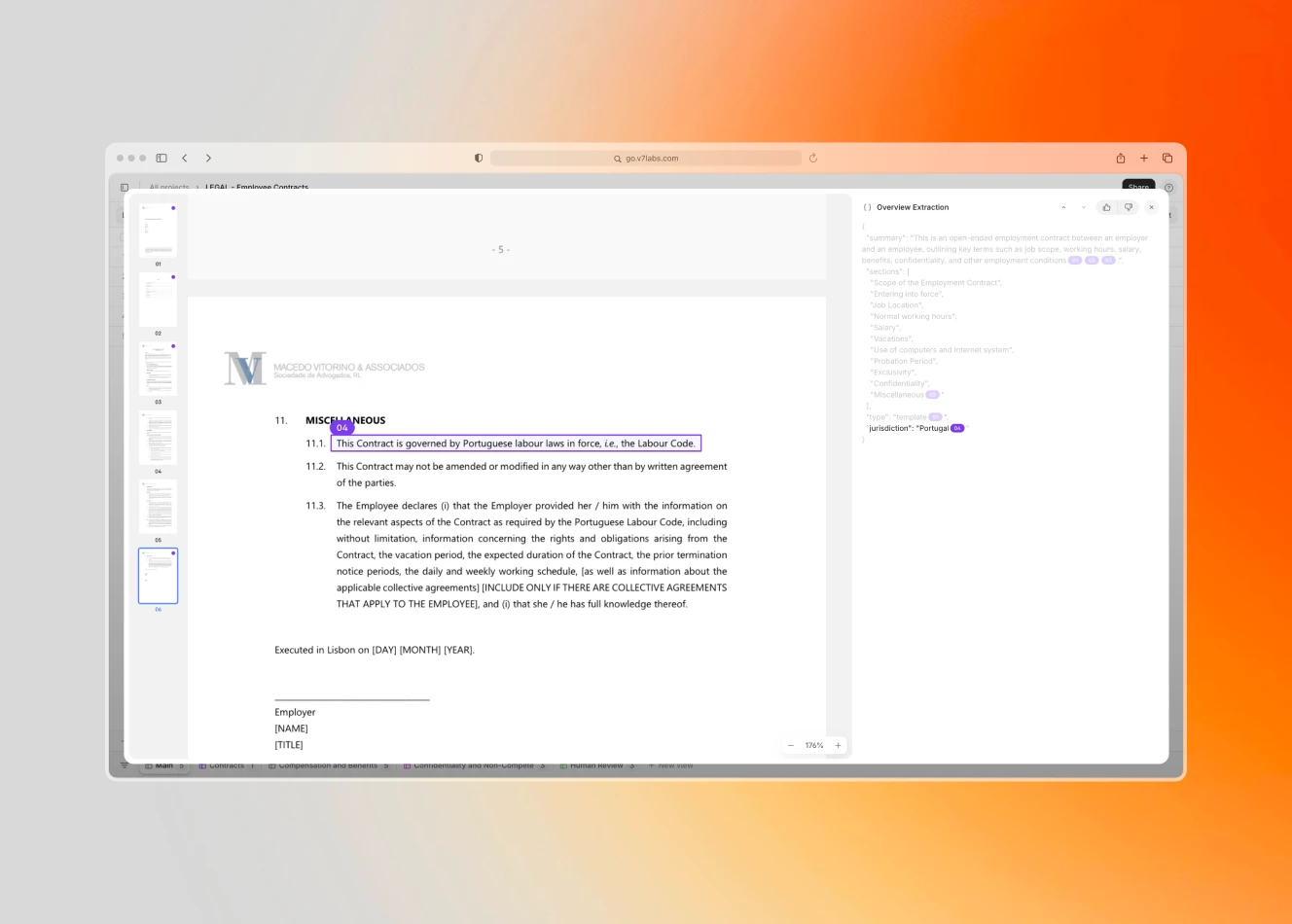
AI legal software of today goes far beyond simple keyword searching. It can highlight relevant legal sources, compare multiple contract versions to spot discrepancies, and flag potentially problematic clauses. The technology helps lawyers focus on strategy and interpretation rather than spending hours scanning documents for specific terms. For example, during due diligence, AI can analyze thousands of contracts simultaneously, identifying non-standard clauses, missing terms, and potential compliance issues across jurisdictions.
Learn more: Top 7 AI Tools for Contract Review: A Comparison of Legal AI
Automated Claims Processing
Document ingestion • Multi-stage verification • Human-in-the-loop QA • Workflow automation • Exception handling • Fraud detection • Payment processing
Insurance claims processing has evolved from purely manual review to a semi-automated system where AI handles routine cases while flagging complex ones for human attention. The key innovation is the ability to maintain human oversight while dramatically increasing processing speed. Document ingestion systems automatically categorize and extract relevant information, while custom automation rules ensure consistent processing across similar claim types. Modern systems can process straightforward claims in minutes rather than days, automatically routing complex cases to specialized adjusters. This hybrid approach has reduced processing costs by 50% while improving customer satisfaction through faster resolution times.
Learn more: Automated Claims Processing: Implementation Guide for Insurance Operations
Loss Run Analysis
Historical data extraction • Risk pattern recognition • Coverage analysis • Claims history processing • Trend analysis • Predictive modeling • Risk scoring
Before providing coverage, insurers need to understand an entity's loss history. AI streamlines this process by automatically extracting and analyzing data from various document types—from incident reports to previous claims records. The technology can spot patterns that might indicate future risks, helping underwriters make more informed decisions. Advanced systems correlate historical claims data with external risk factors, creating comprehensive risk profiles that would be impossible to compile manually. This deeper analysis enables more accurate pricing and better risk management strategies.
Policy Underwriting Automation
Submission triage • Risk assessment • Automated decisioning • Engineering analysis • Data enrichment • Market analysis • Portfolio optimization
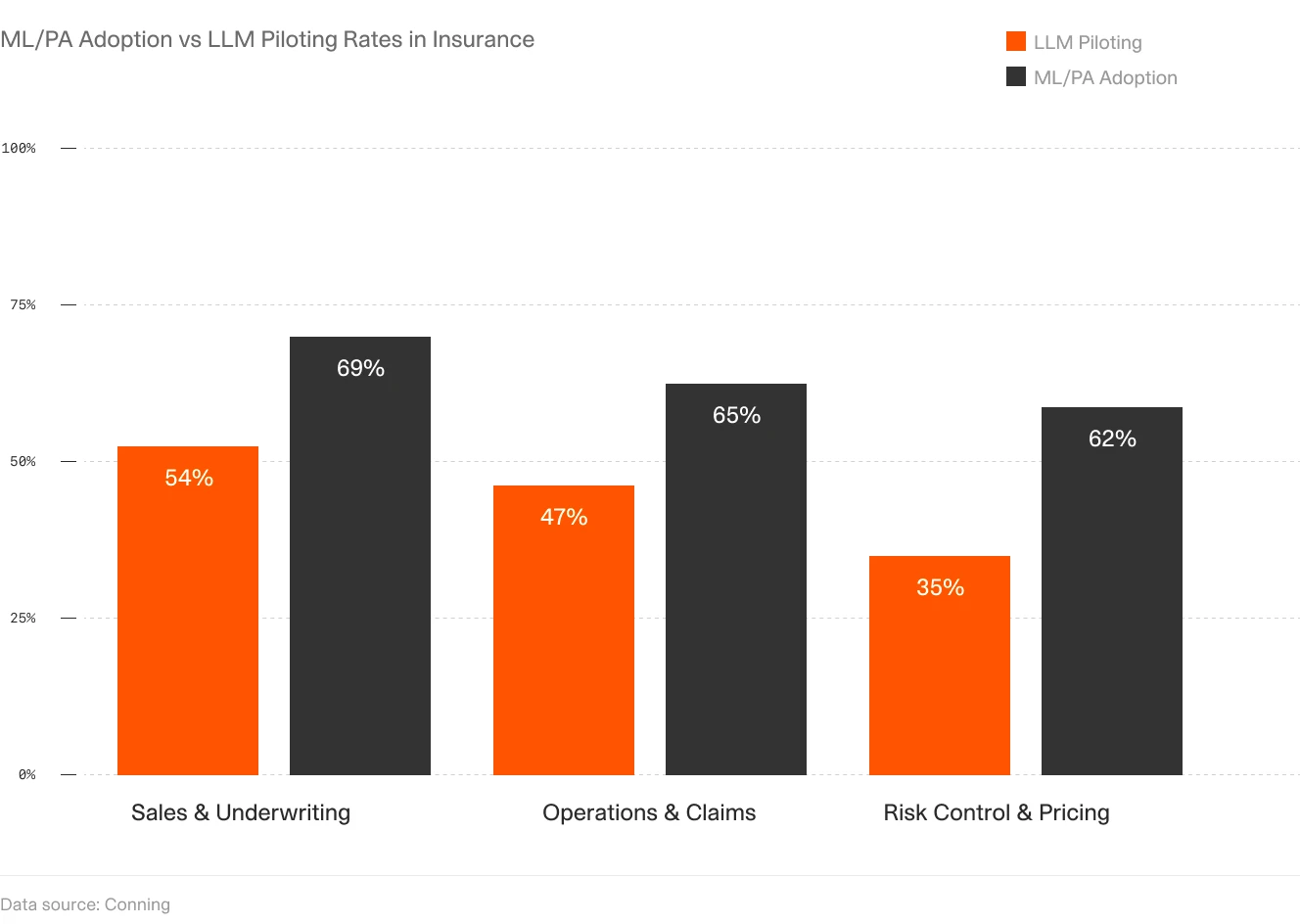
Insurance carriers are automating significant portions of their underwriting processes. More than half of the top companies are piloting the use of large language models in underwriting. AI systems can process new submissions, prioritize them based on risk factors, and route them to the appropriate teams. For simpler policies, the system can even make straightforward underwriting decisions, while more complex cases get flagged for detailed risk engineering analysis. Modern platforms integrate external data sources—from weather patterns to economic indicators. This way, they can provide a more complete risk assessment. This automation has reduced underwriting time from weeks to days for complex policies, and hours to minutes for standard ones, while maintaining or improving risk assessment accuracy.
Learn more: AI for Insurance Underwriting: Key Use Cases & Tools
Finance & Accounting Applications
The finance sector faces unique challenges in processing vast amounts of numerical data while maintaining perfect accuracy and regulatory compliance. AI is reshaping how financial institutions handle everything from routine transactions to complex analysis, bringing both efficiency and new levels of insight. While automation has existed in finance for decades, new AI solutions are taking it far beyond simple rule-based processing.
Balance Sheets and Due Diligence
Financial statement analysis • Anomaly detection • Ratio analysis • Document verification • Regulatory compliance • Audit trail generation • Risk assessment
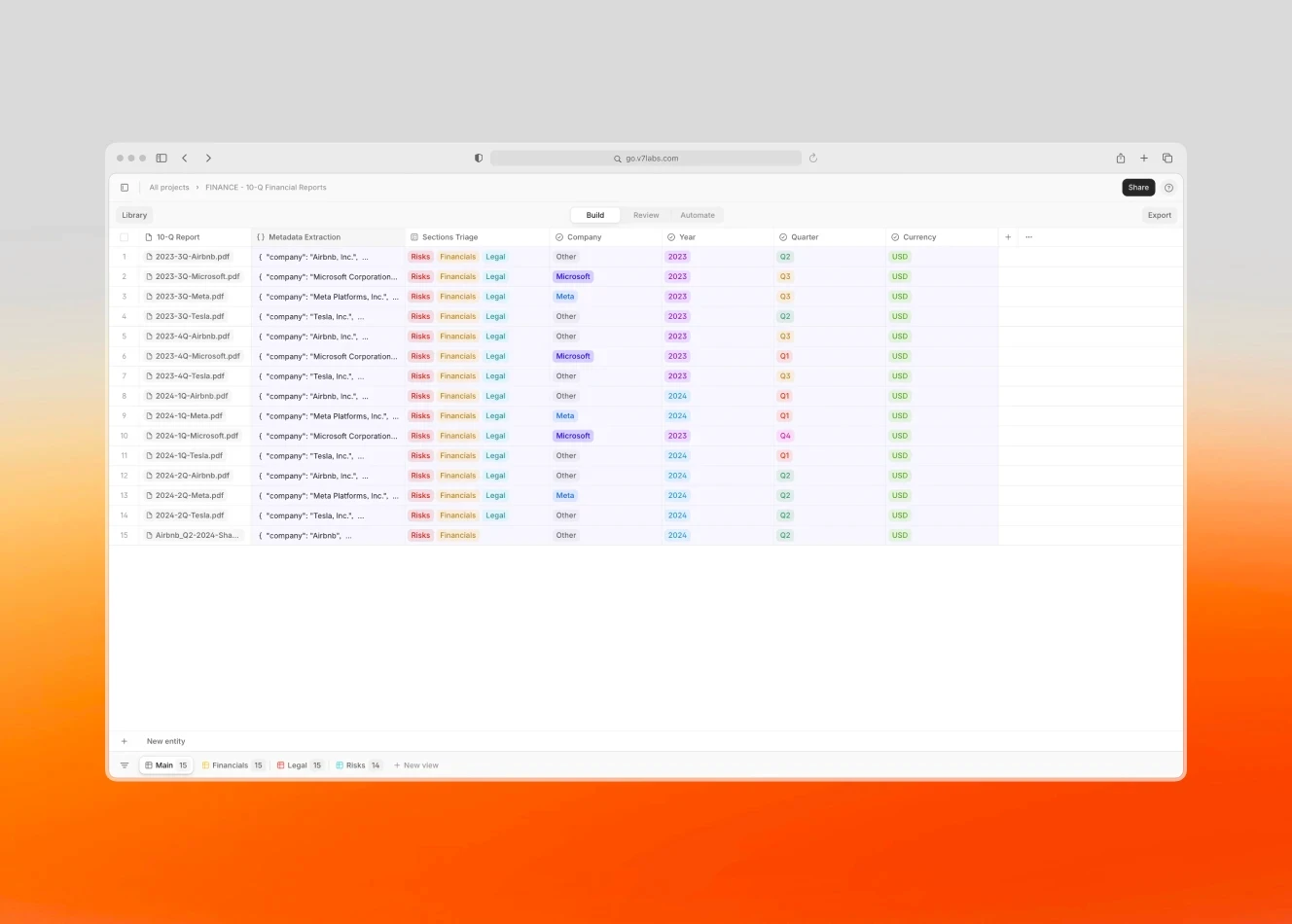
AI software for finance can analyze years of financial statements in minutes, identifying patterns, flagging inconsistencies, and automatically calculating key performance indicators. They don't just spot obvious discrepancies—they can detect subtle patterns that might indicate underlying issues. For instance, AI can analyze thousands of transactions across multiple subsidiaries, identifying inter-company transfers that might affect consolidation or reveal potential regulatory concerns.
Learn more: AI in Due Diligence: What It Means for M&A and Beyond
Loan Application Processing
Credit scoring • Document verification • Risk modeling • Income analysis • Fraud detection • Automated underwriting • Collateral valuation
Traditional loan processing could take weeks; AI has reduced this to hours or even minutes. Advanced systems can automatically verify documents, analyze income patterns, and assess creditworthiness by combining traditional metrics with alternative data sources. They can process multiple document types simultaneously—from tax returns to bank statements—while cross-referencing information to spot discrepancies. The technology particularly shines in small business lending, where it can analyze business health through various data points, from cash flow patterns to industry trends. This has enabled banks to process 5x more applications while actually reducing default rates.
Tax and Payroll Management
Tax code analysis • Compliance monitoring • Automated calculations • Deduction optimization • Multi-jurisdiction processing • Regulatory updates • Exception handling
AI brings unprecedented accuracy and efficiency to tax and payroll operations, as well as employee contract management. Systems can now automatically classify expenses, identify tax savings opportunities, and ensure compliance across multiple jurisdictions. They adapt in real-time to regulatory changes and can handle complex scenarios like multi-state taxation or international payroll requirements. One particularly valuable capability is automated anomaly detection—flagging unusual patterns that might indicate errors or opportunities for tax optimization.
Fraud Detection
Pattern recognition • Transaction monitoring • Behavioral analysis • Network analysis • Real-time alerting • Risk scoring • Case management
Modern AI fraud detection goes far beyond rules-based systems. It uses machine learning to understand normal patterns of financial behavior and identify suspicious deviations in real-time. These systems can analyze thousands of data points simultaneously—from transaction amounts and locations to device IDs and user behavior patterns. They're particularly effective at spotting sophisticated fraud schemes that might escape traditional detection methods. For example, they can identify complex networks of related transactions that might indicate money laundering, even when individual transactions appear normal.
Real Estate & Asset Management Applications
Real estate and asset management have traditionally relied heavily on human expertise and manual analysis. AI is changing this landscape by automating complex valuations, streamlining document processing, and providing deeper market insights. The technology is particularly valuable in commercial real estate, where decisions involve analyzing vast amounts of data across multiple parameters. This potential hasn’t gone unnoticed—according to a recent JLL report, 69% of C-suite corporate real estate leaders report piloting AI initiatives and having a clear AI implementation strategy in place.
Property Appraisal
Automated valuation • Computer vision analysis • Market comparison • Location analytics • Price trend prediction • Risk assessment • Demographic analysis
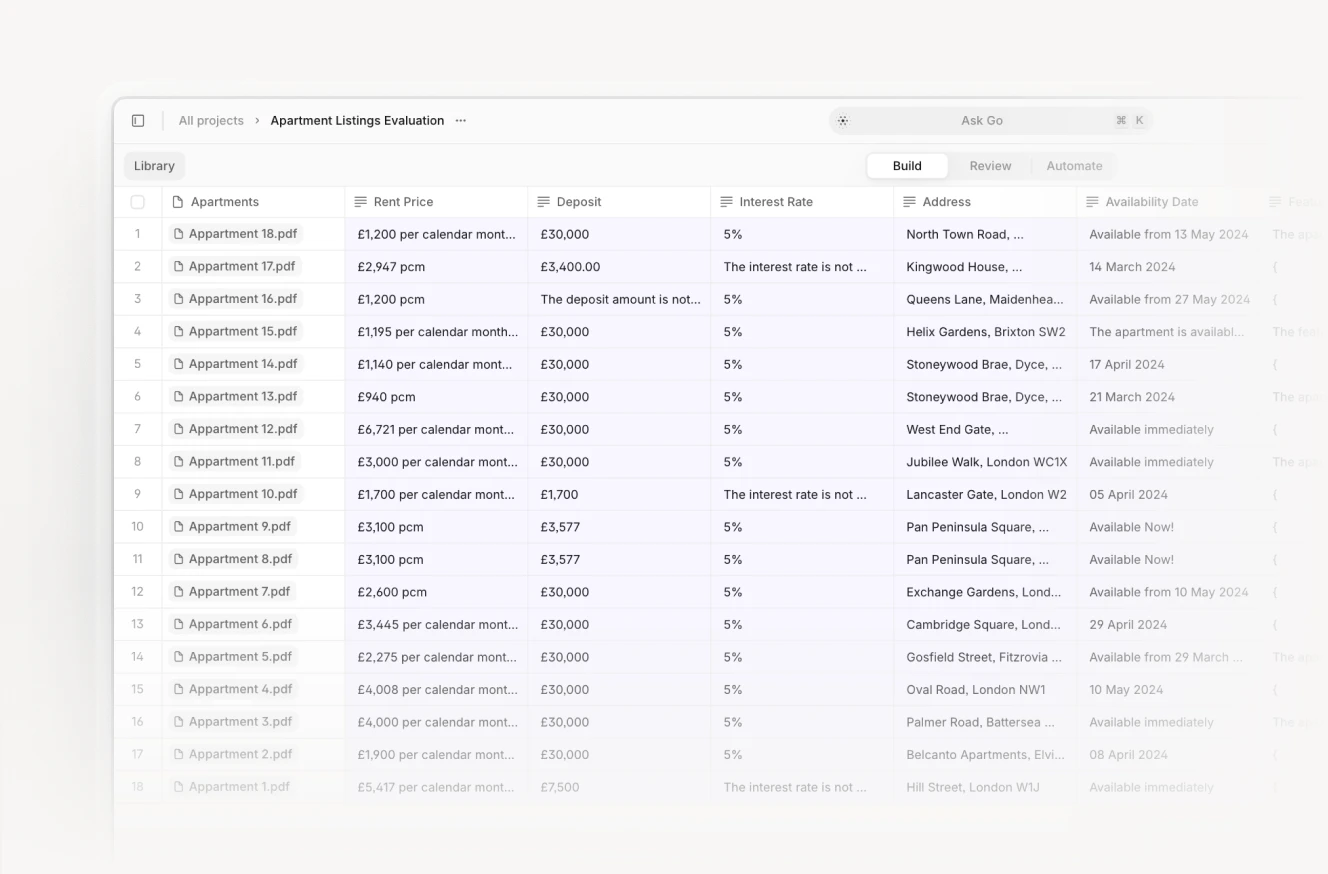
AI has supercharged property valuation by analyzing hundreds of factors simultaneously. Modern systems combine traditional metrics like square footage and location with alternative data sources—from satellite imagery to local business patterns. They can assess property condition from photographs, analyze neighborhood development trends, and predict future value changes. The technology is particularly powerful in commercial real estate, where it can evaluate complex factors like foot traffic patterns and local market dynamics.
Investor Reporting
Performance analytics • Portfolio visualization • Risk monitoring • Automated report generation • Customizable dashboards • Regulatory compliance • Scenario analysis
Investment reporting has evolved from static monthly updates to dynamic, real-time analysis. AI systems automatically gather data from multiple sources, standardize it, and generate comprehensive reports tailored to different stakeholder needs. They can track performance across diverse asset types, identify emerging risks, and simulate various market scenarios. The technology is particularly valuable for large portfolios, where it can spot subtle patterns and correlations that might affect overall performance.
Learn more: De-risking Asset Management with AI: A Strategic Guide for Investment Firms
Lease Agreement Analysis
Contract extraction • Clause comparison • Risk identification • Obligation tracking • Compliance monitoring • Term optimization • Payment analysis
AI brings unprecedented efficiency to lease management by automatically extracting and analyzing key terms from lease documents. Systems can compare hundreds of leases simultaneously, identify non-standard clauses, and track critical dates and obligations. They're particularly effective at handling complex commercial leases with numerous variables and conditions. AI lease agreement management technology can also analyze payment histories and tenant behaviors to predict potential issues before they arise. Large property managers report faster lease processing and reduction in missed obligations.
Commercial Real Estate Listings
Image-text correlation • Market analysis • Listing optimization • Recommendation engines • Search enhancement • Property matching • Automated descriptions

Modern AI solutions for real estate can analyze property photos and automatically generate accurate descriptions, compare listings across multiple parameters, and create sophisticated matching algorithms based on buyer preferences. The technology excels at understanding subtle market positioning—for instance, automatically identifying and highlighting features that command premium prices in specific markets. These platforms include advanced recommendation engines that can suggest properties based on complex combinations of criteria. The systems also optimize listing visibility through targeted placement and automatic updates based on market response.
Learn more: https://www.v7labs.com/go/automations/commercial-real-estate-listings
Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals Applications
Healthcare and pharmaceutical industries face unique challenges in balancing cutting-edge technology with patient care and safety requirements. AI is proving particularly valuable in areas requiring both high accuracy and rapid processing of complex data. From clinical applications to operational efficiency, the technology is helping healthcare providers deliver better patient outcomes while managing costs.
Lesion Detection in Radiology
Medical image segmentation • Anomaly detection • Diagnostic assistance • 3D reconstruction • Measurement automation • Report generation • Clinical workflow integration
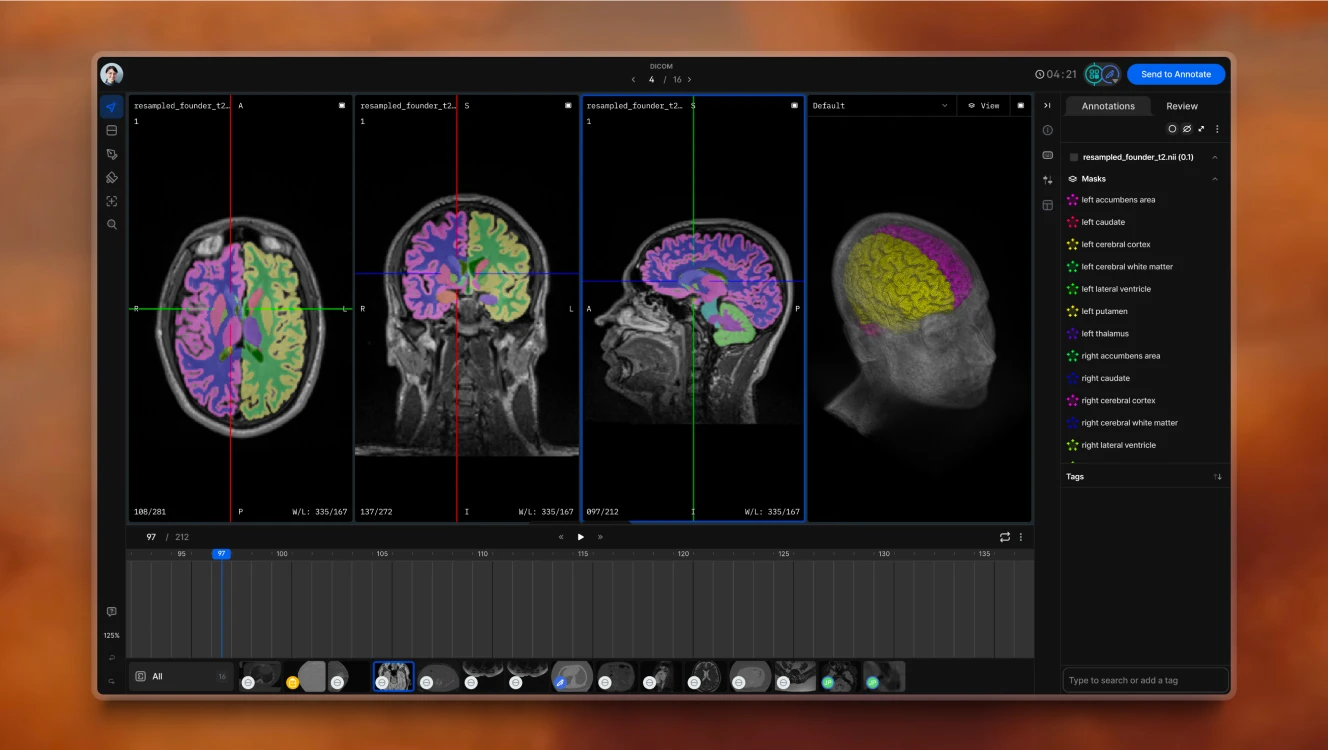
AI has improved radiology workflows by providing reliable first-pass analysis of medical images. Modern systems can automatically detect and segment various abnormalities in CT, MRI, and X-ray images—from potential tumors to subtle changes in tissue density. The latest generation of AI medical image annotation tools, combined with data labeling services, has significantly simplified the development of such models while greatly improving their accuracy. Beyond simple detection, these solutions provide precise measurements and 3D visualizations, helping radiologists make more accurate assessments. This technology has created new opportunities for healthcare technology manufacturers and software developers, who can now offer specialized AI solutions for specific medical imaging applications.
Learn more: AI in Radiology: Pros & Cons, Applications, and 4 Examples
Medical Records Analysis
Document digitization • Cross-reference verification • Patient history analysis • Clinical data extraction • Treatment pattern recognition • Compliance verification • Interoperability management
The challenge of managing diverse medical documentation has found a powerful solution in AI. Modern systems can process and analyze various document types—from handwritten prescriptions to complex surgical reports—creating standardized, searchable records. They excel at cross-referencing information across different sources, automatically flagging inconsistencies or potential drug interactions. The technology can analyze years of patient records in seconds, identifying treatment patterns and potential complications that might be missed in manual review.
WSI Analysis and Digital Pathology
Tissue classification • Cell counting • Morphological analysis • Parasite detection • DNA pattern recognition • Quality control • Research automation
Whole Slide Imaging (WSI) analysis represents a major breakthrough in pathology and pharmaceutical research. AI systems can analyze microscopic images with unprecedented speed and accuracy, identifying cell types, counting organisms, and detecting subtle patterns in tissue samples. This capability is particularly valuable in drug development, where it can rapidly analyze thousands of samples to assess treatment effectiveness. The technology also enables more efficient quality control in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where it can detect contamination or irregularities in production samples.
Learn more: How to Annotate Digital Pathology Images for AI
Drug Labels and Compliance Data
Regulatory monitoring • Label verification • Compliance tracking • Documentation automation • Safety monitoring • Change management • Global regulation alignment
AI brings new efficiency to the complex world of pharmaceutical compliance and labeling. Modern systems can automatically track regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions, ensure label accuracy, and maintain comprehensive compliance documentation. They're particularly valuable in managing updates to drug information and safety data, automatically identifying required changes and ensuring consistent implementation across all documentation. The technology can also monitor adverse event reports and safety signals, helping pharmaceutical companies respond more quickly to potential issues.
Retail & E-Commerce Applications
The retail sector faces constant pressure to reduce costs while improving customer experience across both physical and digital channels. AI is helping retailers tackle these challenges by automating routine operations and providing deeper customer insights. From preventing theft to streamlining purchases, the technology is changing how stores operate and interact with customers.
Shrinkage Prevention
Video analytics • Behavioral analysis • Inventory tracking • Pattern recognition • Real-time alerting • POS integration • Staff monitoring
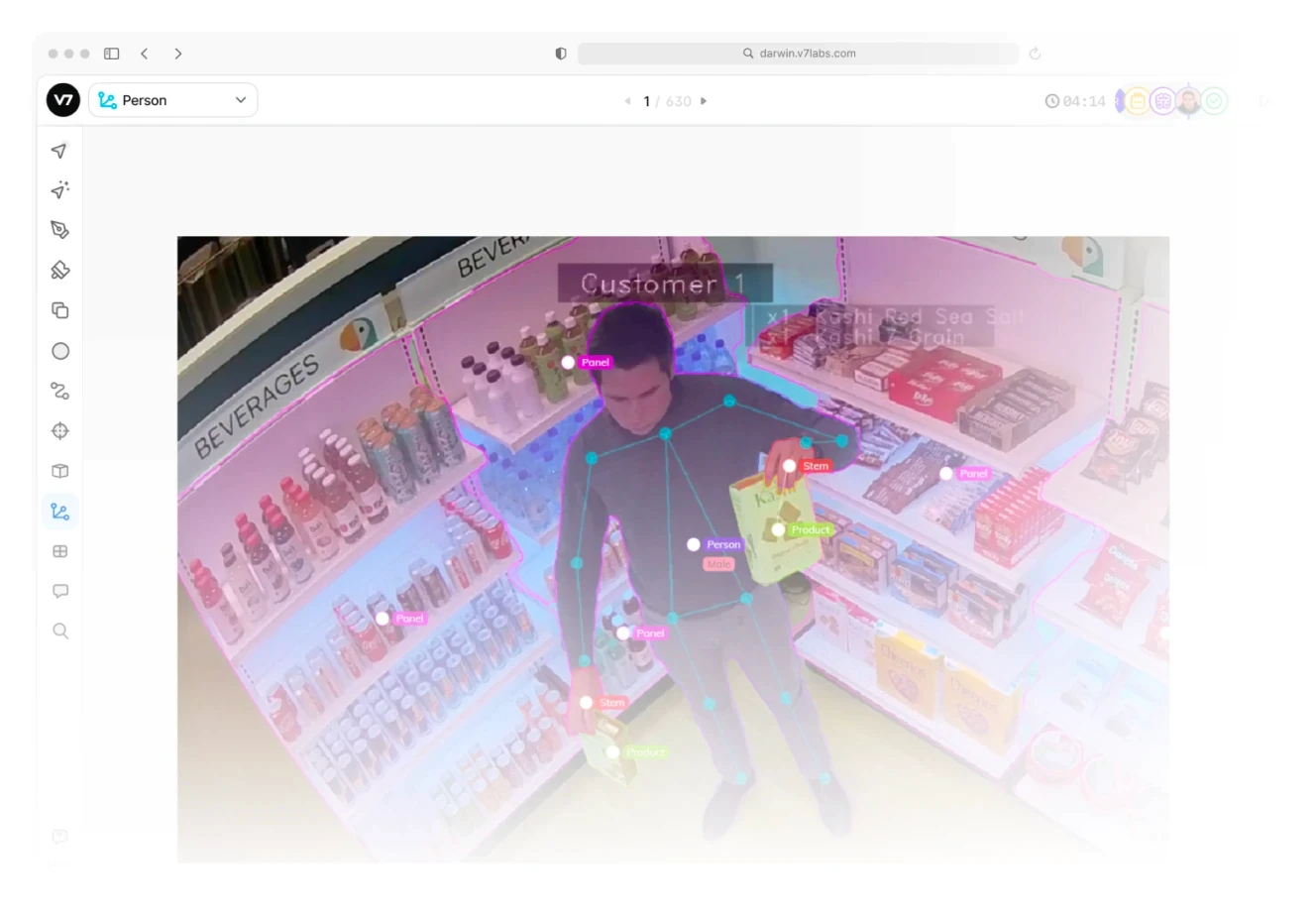
Modern retail security goes far beyond traditional surveillance cameras. AI-powered systems can identify suspicious behavior patterns in real-time, from unusual product handling to questionable checkout activities. This is possible thanks to video annotation software that can "teach" computers to understand what happens in videos and to train custom computer vision models. These models can integrate with inventory systems to track product movement and can detect common theft techniques like label switching or ticket switching. AI solutions using human posture and activity recognition can detect and flag suspicious behavior using standard industrial camera feeds. Major retail chains using these systems report a significant reduction in shrinkage while simultaneously reducing false alerts. The technology is particularly effective at identifying organized retail crime patterns that might go unnoticed in traditional security setups.
Learn more: Building & Scaling ML Solutions for Big Box Retail
AI Order Management
Order routing • Inventory optimization • Fulfillment automation • Customer communication • Status tracking • Returns processing • Stock prediction
AI changed order management from a linear process to an intelligent system that can make real-time decisions. Modern platforms automatically route orders to optimal fulfillment locations based on multiple factors—from inventory levels to shipping costs and delivery times. They coordinate across departments, manage inventory levels, and handle customer communications automatically. The technology is particularly valuable in managing complex scenarios like split shipments or custom orders.
Self-Checkout Solutions
Product recognition • Weight verification • Loss prevention • Customer assistance • Payment processing • Exception handling • Queue management
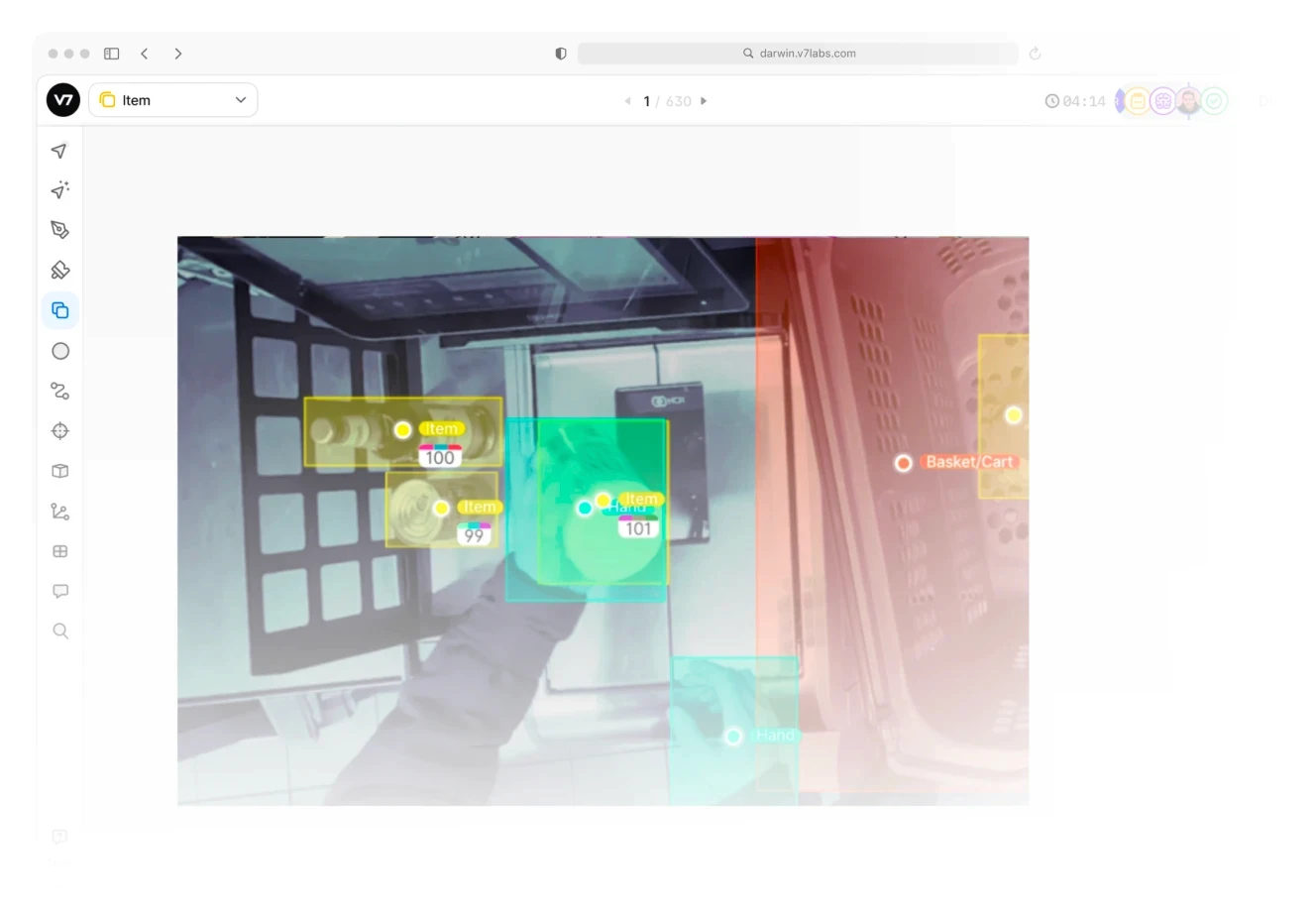
AI-powered self-checkout systems represent a major leap beyond traditional barcode scanning. Computer vision technology can identify products, detect scanning errors, and prevent common theft techniques. These systems can process multiple items simultaneously and understand product variations. They integrate with store security systems and can alert staff to potential issues while maintaining smooth customer flow.
AI Sentiment Analysis
Review analysis • Brand monitoring • Feedback categorization • Trend detection • Crisis prediction • Customer satisfaction tracking • Competitive analysis
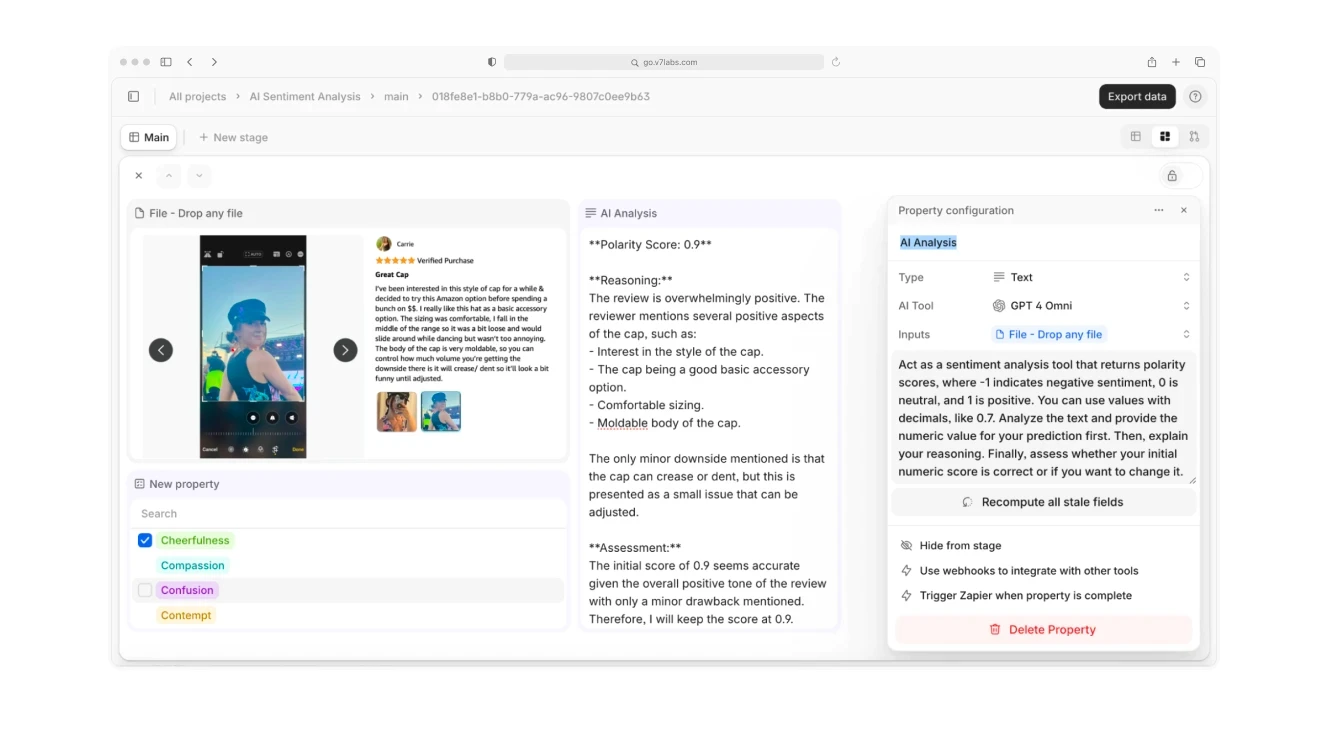
AI systems can analyze customer feedback across multiple channels—from social media to product reviews—understanding context and identifying specific issues or trends. They can detect potential reputation risks before they escalate and track customer satisfaction across different product lines or store locations. The technology is particularly valuable in identifying emerging customer preferences and competitive threats. Retailers using these AI sentiment analysis techniques report 50% faster response to customer issues and 40% improvement in problem resolution rates.
Manufacturing & Energy Applications
Manufacturing and energy sectors are experiencing a fundamental shift through AI adoption, particularly in quality control and infrastructure maintenance. These industries require consistent monitoring of complex systems and quick identification of potential issues—areas where AI excels. The technology is helping companies move from reactive to predictive operations management.
Production Line Defect Detection
Computer vision inspection • Real-time monitoring • Quality control automation • Defect classification • Process optimization • Yield improvement • Specification compliance
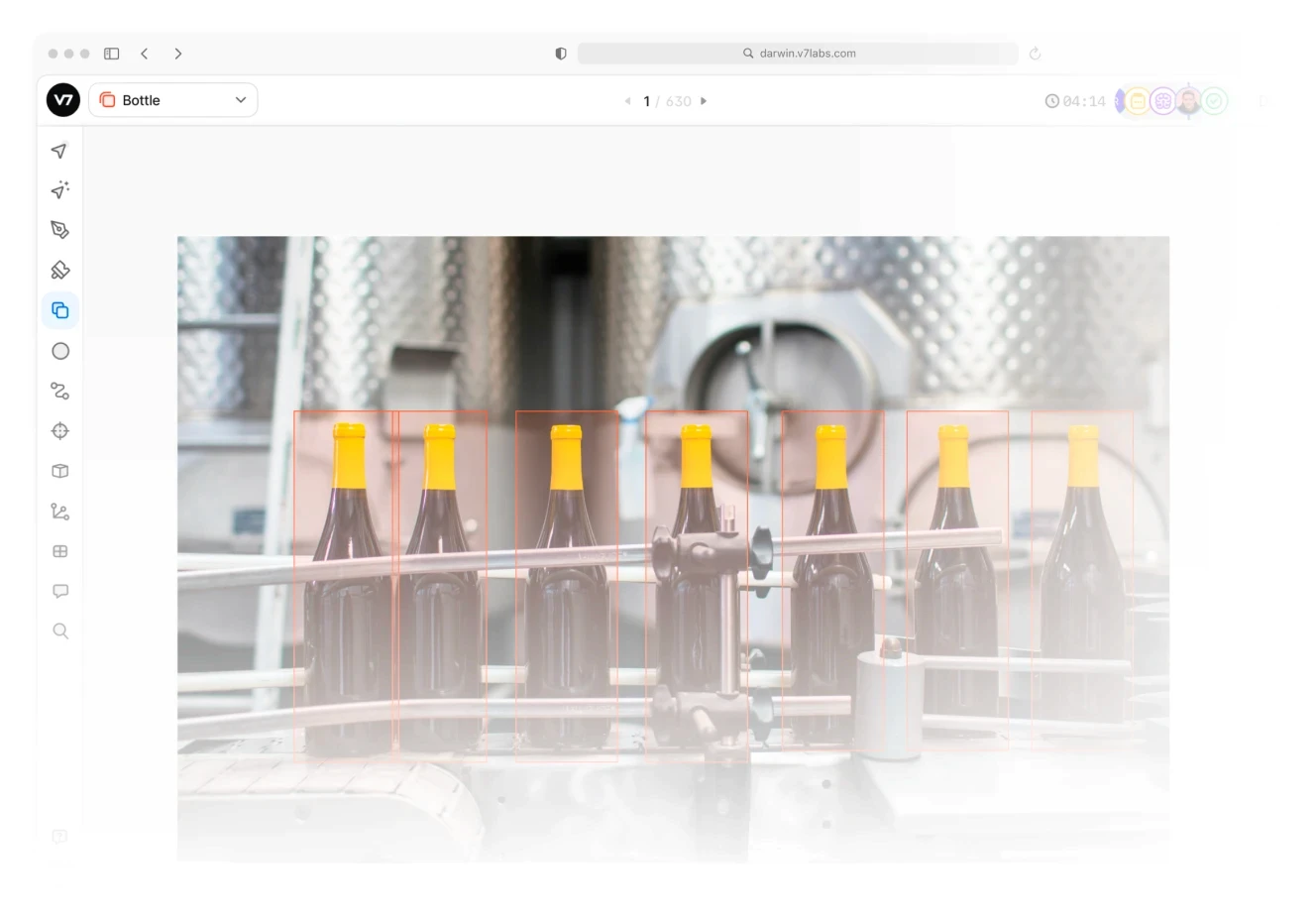
AI improved quality control in manufacturing by enabling 100% inspection rather than random sampling. Modern systems can detect defects invisible to the human eye, from microscopic cracks to subtle color variations, at full production speed. They can identify patterns that indicate emerging problems before they cause major issues, allowing preventive maintenance. For example, automotive manufacturers using AI inspection systems report 90% detection rates for subtle defects while processing thousands of components per hour. The technology particularly shines in detecting complex defect patterns that might indicate systemic production issues.
Learn more: 7 Out-of-the-Box Applications of AI in Manufacturing
Energy Audit Reports
Consumption analysis • Efficiency modeling • Cost optimization • Carbon footprint tracking • Usage pattern detection • ROI calculation • Regulatory compliance
AI brings new depth to energy auditing by analyzing complex usage patterns and identifying optimization opportunities that might be missed in traditional audits. Modern systems can process data from thousands of sensors simultaneously, identifying inefficiencies in real-time and suggesting specific improvements. They're particularly effective at optimizing energy use across large facilities or multiple sites, taking into account factors like weather patterns, production schedules, and energy prices.
Predictive Maintenance and Infrastructure Inspection
Condition monitoring • Failure prediction • Drone-based inspection • Thermal analysis • Wear pattern detection • Maintenance scheduling • Asset lifecycle optimization
Companies like Raptor Maps use drone-captured imagery analyzed by AI to detect panel damage, soiling, and performance issues across vast solar farms. By using an AI data labeling platform, they reduced model development time by 83%, making custom model training faster and more efficient. These models can identify issues ranging from dirt accumulation to complex electrical problems, enabling targeted maintenance. This technology has significantly lowered inspection costs while improving problem detection rates. In manufacturing, similar AI-driven systems analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures weeks in advance, helping reduce unplanned downtime and optimize maintenance schedules.
Transportation & Logistics Applications
The transportation and logistics sector faces increasing pressure to improve efficiency while managing rising costs and complex supply chains. AI is helping companies overcome these challenges by automating document processing, optimizing routes, and enhancing vehicle operations. The technology is particularly valuable in connecting different parts of the logistics chain into a more coherent, efficient system.
Shipping Label Processing
OCR enhancement • Address validation • Package classification • Routing optimization • Compliance verification • Exception handling • Automated sorting
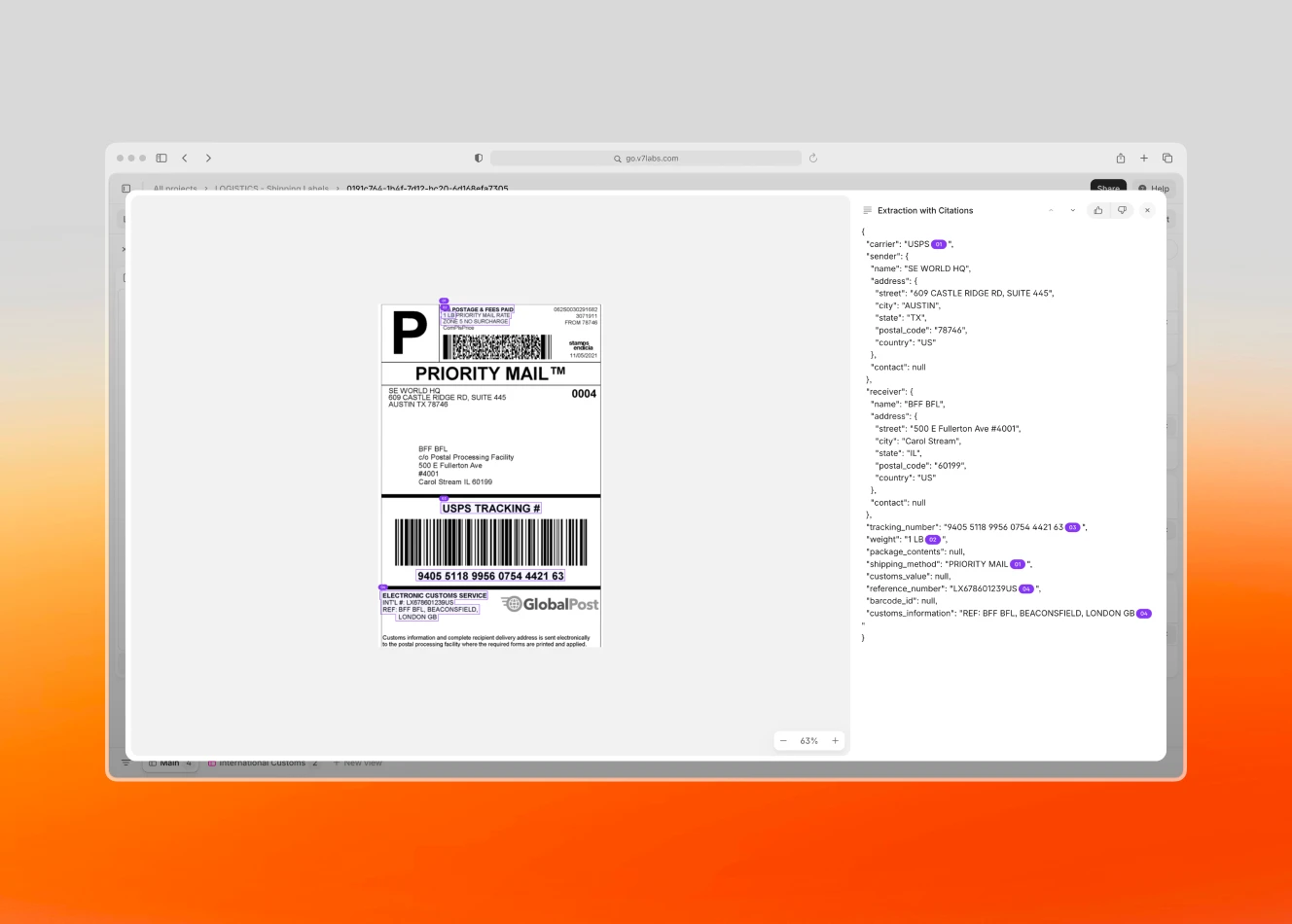
AI can read and process shipping labels in any condition—damaged, partially obscured, or poorly printed—with great accuracy rates. They automatically validate addresses, classify packages for optimal routing, and flag potential compliance issues. The technology is particularly valuable in high-volume operations, where it can process thousands of labels per hour while reducing error rates. This means faster processing times and reduction in misrouting incidents.
Learn more: How to Automate Shipping Label Processing with Generative AI
Freight Cost Analysis & Invoice Management
Rate optimization • Cost prediction • Invoice verification • Anomaly detection • Carrier performance tracking • Budget forecasting • Contract compliance
AI brings new precision to freight cost management by analyzing complex pricing patterns and identifying optimization opportunities. Modern systems can automatically audit freight invoices, detecting discrepancies and ensuring compliance with contracted rates. They're particularly effective at handling complex pricing scenarios involving multiple carriers and routes. The technology can predict future shipping costs with remarkable accuracy, helping companies optimize their logistics budgets.
Autonomous Driving and AI-Assisted Solutions
Route optimization • Safety monitoring • Fuel efficiency • Predictive maintenance • Driver assistance • Traffic pattern analysis • Fleet management
While fully autonomous vehicles are still evolving, AI is already changing vehicle operations through advanced driver assistance and fleet management systems. These technologies combine real-time sensor data with predictive analytics to improve safety and efficiency. For instance, AI systems can predict traffic patterns, optimize routes dynamically, and monitor driver behavior to prevent accidents. The technology is particularly effective at managing large fleets, where it can coordinate multiple vehicles while adapting to changing conditions in real-time.
Construction & Engineering Applications
The construction and engineering sectors are embracing AI to address long-standing challenges in safety, project management, and quality control. As projects become more complex and safety standards more stringent, AI provides new capabilities for monitoring, documentation, and risk management. The technology is particularly valuable in combining different types of data to prevent problems before they occur.
Safety and PPE Detection
Real-time monitoring • Compliance tracking • Risk zone identification • Behavior analysis • Equipment verification • Alert generation • Incident prevention
Construction sites present unique safety challenges that AI is particularly well-suited to address. Modern systems use computer vision to monitor PPE compliance in real-time, detecting when workers are missing required safety equipment or entering hazardous areas without proper protection. They can identify unsafe behaviors or conditions before accidents occur, from improper equipment usage to dangerous site conditions. The technology is especially valuable in large sites where manual monitoring would be impractical.
Site Inspection Report Automation
Visual documentation • Progress tracking • Defect detection • Compliance verification • Report generation • Issue classification • Historical comparison
AI can process thousands of site photos and sensor readings, automatically generating detailed inspection reports that would take teams of engineers days to compile. They're particularly effective at tracking project progress against plans, identifying potential issues early, and maintaining comprehensive documentation for compliance purposes. The technology is very good at comparing current site conditions against both plans and historical data, providing early warning of developing problems.
Bidding Documents Analysis
Cost estimation • Risk assessment • Requirement extraction • Comparison analysis • Historical modeling • Resource planning • Compliance verification
AI brings new precision to the complex process of analyzing and preparing bid documents. Modern systems can automatically extract key requirements, compare them against historical project data, and identify potential risks or opportunities that might affect pricing. They're particularly effective at analyzing complex technical specifications and identifying discrepancies or missing information that could impact project success.
From Idea to Impact: Making AI Work for Your Business
Successful AI adoption in business flows from clear operational needs rather than technological possibilities. Through our examination of cases ranging from the European company's costly custom model development to effective targeted implementations, one principle stands clear: business problems should drive AI adoption, not the other way around.
Several critical insights emerge:
Proven use cases first: Data processing, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics offer reliable starting points for AI implementation.
Leverage existing solutions: Many business needs can be addressed through established AI platforms and tools, often outperforming custom development in both cost and effectiveness.
Maintain pragmatism: Match AI capabilities to specific business needs for maximum impact.
Embrace human-AI synergy: The most successful implementations amplify human capabilities, freeing professionals to tackle higher-value challenges.
Companies that thrive with AI focus on creating tangible business value through targeted applications. Their success comes from methodical implementation: starting small, proving value in well-defined areas, and building on each success.
Ready to optimize your business operations with AI? Book a consultation and send us some examples of your data to explore practical applications for your specific challenges.