AI implementation
AI in Cybersecurity: 5 Crucial Applications
10 min read
—
Apr 1, 2023
How does AI benefit cybersecurity? Are AI-enabled cybersecurity systems more resilient against malware than manual detection systems? Learn more about the top applications of AI in cybersecurity.

Guest Author
The importance of cybersecurity is growing along with technological progress.
According to FBI Internet Crime Report 2021, the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) received 847,376 complaints of internet-related crimes. They resulted in staggering financial losses of 6.9 billion dollars, compared to 4.2 billion in 2020.
Hackers, malicious agents, or cyber attackers constantly try to breach digital spaces. Cyber crimes such as phishing, scams, or data and identity theft are rising. To prevent these attacks, organizations employ qualified cybersecurity teams that work tirelessly to secure digital systems, leveraging new technologies, including artificial intelligence.
AI in cybersecurity analyzes system usage patterns to identify potentially malicious activities or threat actors and predict cyber attacks before they happen. AI-enabled automated monitoring protects systems 24/7 and enables organizations to take preventive measures before harm is done.
Some major AI in cybersecurity applications include:
Malware & phishing detection
Knowledge consolidation
Detection & prioritizing new threats
Breach risk prediction
Task automation
But before we explore these applications in detail, let’s briefly look at the current state of AI in cybersecurity below.
AI in cybersecurity: An overview
AI in cybersecurity has been gaining traction over the past years. The idea of mitigating cybersecurity risks before they occur has been bringing in investments to develop and improve AI-powered cybersecurity systems.
The latest report by Verified Market Research suggests that the market size for Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity stood at 7.58 billion dollars in 2022 and is expected to reach 80.83 billion by 2030.

AI in cybersecurity market size 2022-2030 (source)
These growing numbers are not surprising since hackers also get access to new technologies.
For instance, about 93.67% of malware observed in 2019 could modify its source, which made it nearly impossible to detect. Moreover, reportedly 53% of consumer PCs and 50% of commercial computers were re-infected with malware after a brief recovery period.
The increasing number of cyber-attacks has brought the international community's attention toward the possible use of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity. According to a survey by The Economist Intelligence Unit, 48.9% of global executives and leading security experts believe that AI and machine learning are best equipped for countering modern cyber threats.
Moreover, a report by Pillsbury, a global law firm focusing on technology, asserted that 44% of global organizations already implement AI to detect security intrusions.
Now, let's look at some of the most significant applications of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity.
Malware & phishing detection
Malware is malicious software transferred to a user's computer (usually over a network) and designed to carry out unauthorized operations. Some common malware activities include:
Data deletion
Creating unnecessary copies
Data encryption
Accessing and controlling a device remotely
Malicious advertising
Monitoring user activity (spyware)
Ransomware attacks
Malware is considered a ransomware attack if the attacker intends to demand a ransom amount in exchange for giving the files or system access back to the owner. While modern tools efficiently detect conventional malware or ransomware attacks, dynamically changing malicious agents are much more challenging to filter out.
AI-based cybersecurity systems can detect malicious traits more effectively. Chuck Everette, director of cybersecurity advocacy at Deep Instinct, claims that while legacy signature-based malware detection systems effectively prevent 30% to 60% of threats, AI-powered systems have a security efficiency rate of 80% to 92%.
AI researchers and security experts employ numerous techniques. For instance, research at Plymouth University tackled malware detection using computer vision. They used binary visualization analysis to convert files into colored image representations showing a clear color distinction between malicious and benign files.
Using neural networks, the researchers achieved an overall malware detection accuracy of 74% on all file formats, with as much as 91.7% and 94.1% accuracy for .doc and .pdf files.
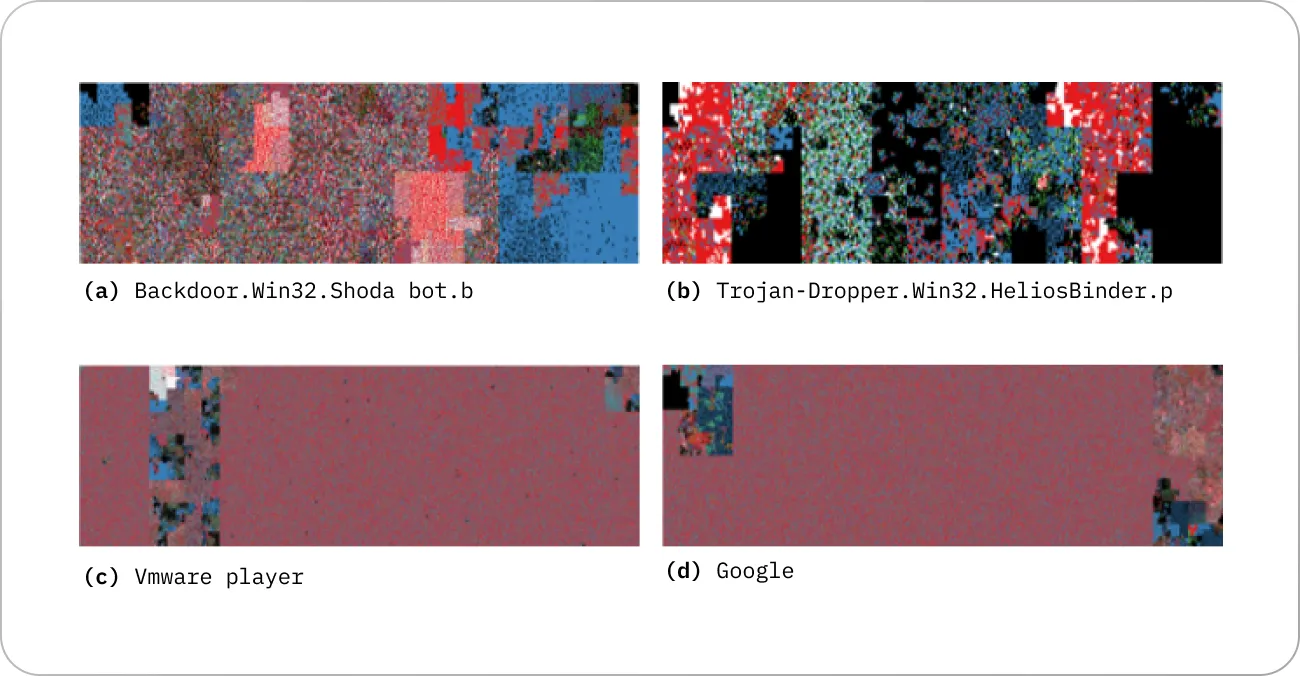
Binary visual comparison of malicious files (a) and (b) against normal files (c) and (d) (source)
Ready to start training models for image classification and detection tasks? Check out how you can turn training data into models with the V7 platform
Phishing attacks
Another common method for hackers to deploy and activate malware is phishing attacks. Phishing refers to the hacker sending malicious links to users (usually via emails) to acquire sensitive information or disrupt the system. The malware is activated when the user clicks on the malicious link.
AI-based systems can detect whether a website or email is a phishing trap. Researchers from the University of North Dakota proposed a phishing detection technique based on machine learning that analyzes the structure of emails and classifies them as legitimate or phishing emails. Using 4000 training samples, the researchers achieved an accuracy of 94%.
Interested in building AI for document extraction? check out our guide to intelligent document processing AI
Another example of an effective AI-enabled phishing detection tool includes Mimecasts's CyberGraph, which uses machine learning to prevent impersonation or phishing attacks. It includes three major capabilities:
Blocking trackers embedded into emails that can disclose confidential information
Identifying patterns using identity graphs to detect phishing emails
Alerting users with dynamic color-coded warning banners that signify threat level
Another prominent leader in the cyber security domain is Cofense, which has acquired Cyberfish, a provider of AI systems for phishing protection. Their combined knowledge of machine learning, computer vision, and detection and response creates a real-time protection system.
Artificial intelligence also can analyze malware based on its inherent characteristics, e.g., if the software is designed to delete or encrypt files without authorization, it is most likely a threat.
Knowledge consolidation
Any online system is vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. Preventing them requires implementing and complying with hundreds of security protocols and standards.
Cybersecurity professionals cannot keep up with the thousands of existing software vulnerabilities, which is why manual threat detection always carries the risk of security leaks.
Luckily, ML-enabled security systems can help minimize human error. Machine learning models can retain information from decades-old data and use the consolidated knowledge to detect security breaches.
A prime example of consolidated learning is the IBM Watson platform. IBM security teams have constantly promoted Watson for advanced cybersecurity provisions. Its threat detection model is trained on millions of data points, and the cognitive learning capabilities combine computer and human intelligence for automating threat detection and reducing security incidents.
Detecting & prioritizing new threats
With the growing complexity of software architectures, the possibility of new vulnerabilities also increases. According to Statista, over 22,000 new vulnerabilities were registered in 2022 alone, the highest reported figure since 2009.
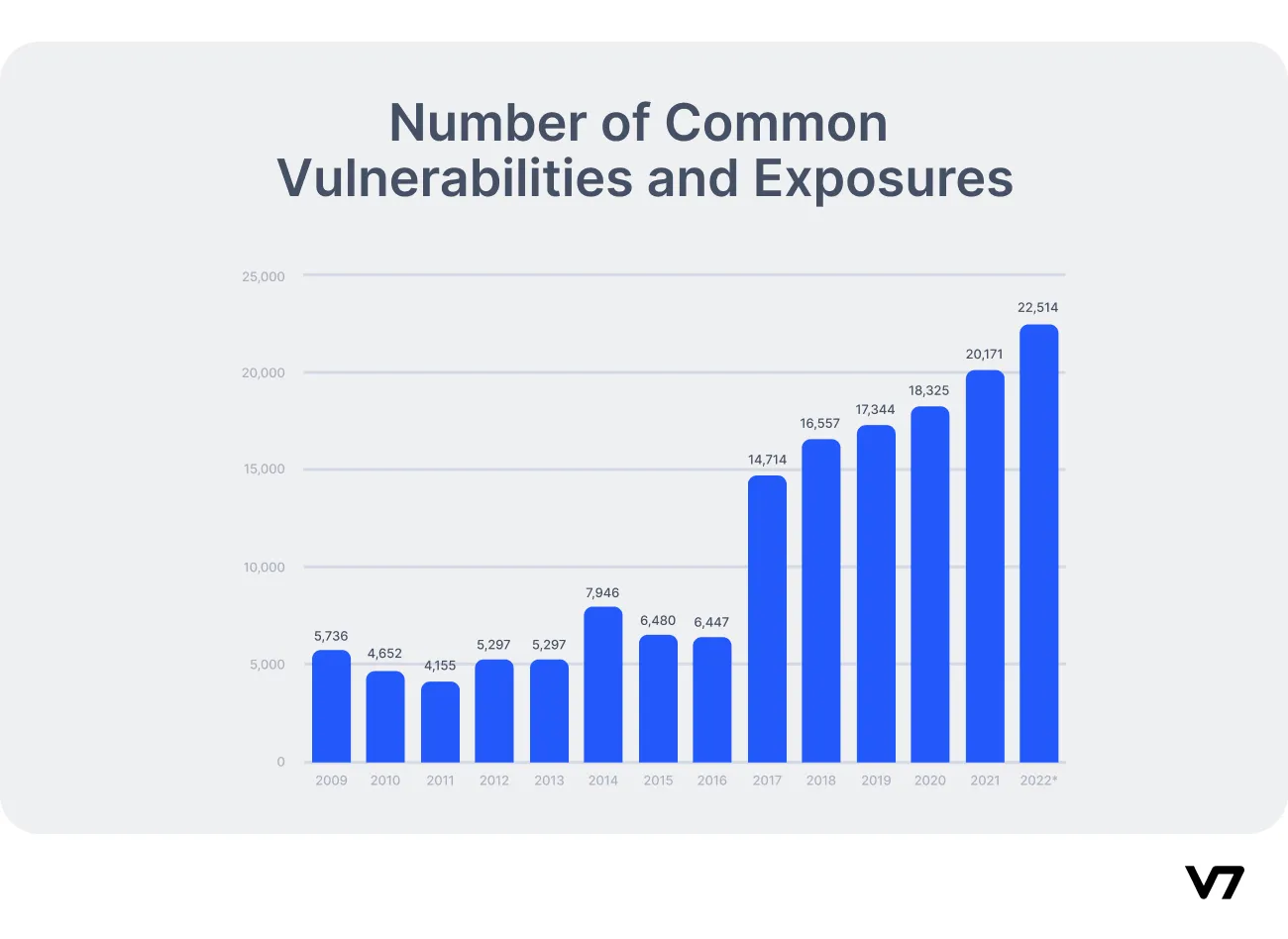
Software vulnerabilities per year 2009—2022 (source)
As mentioned above, cybersecurity professionals can’t keep up with all the possible digital threats. However, machine learning-based cybersecurity systems can keep track of all global and industry-specific vulnerabilities. AI models are constantly updated with data on the latest threats and vulnerabilities, which helps them defend against new threat actors and prevent upcoming attacks.
The success of AI in cybersecurity has encouraged tech giants such as Google, IBM, and Microsoft to develop advanced AI systems for threat identification and mitigation. In 2021, Google committed to spend $10 billion over the next five years to advance cybersecurity through various programs. Their Project Zero team finds and fixes web vulnerabilities to make the internet safer. Moreover, Google Play Protect regularly scans over 100 billion apps for malware and other cyber threats.
Microsoft's Cyber Signals program uses AI to analyze 24 trillion security signals, 40 nation-state groups, and 140 hacker groups to detect malicious activity and software-related weaknesses. According to Microsoft's report, the Cyber Signals program blocked over 35.7 billion phishing attacks and 25.6 billion identity theft attempts on enterprise accounts.
Breach risk prediction
Large enterprises have an extensive IT asset inventory, and analyzing every component for security breach risk is complex. AI tools can identify the components most susceptible to a breach and even predict the expected attack types.
Researchers have proposed cognitive learning-based models that monitor security access points for authorized logins. The model can detect remote hacks early, alert users, and create additional security layers to prevent a possible data breach.
Early information on hacks and breaches can help organizations allocate resources and tools more effectively to prepare for future attacks and develop significant cyber resilience.
Task automation
When dealing with cyber threats, every second counts. The longer the countermeasures take, the more damage is done. A manual threat detection and mitigation process gives an attacker ample time to encrypt or steal data, cover up their tracks, and leave backdoors inside your system.
AI can automate threat detection and take necessary measures immediately. According to IBM, using AI methodologies, the time taken to detect and act against cyber threats can be reduced by 14 weeks.
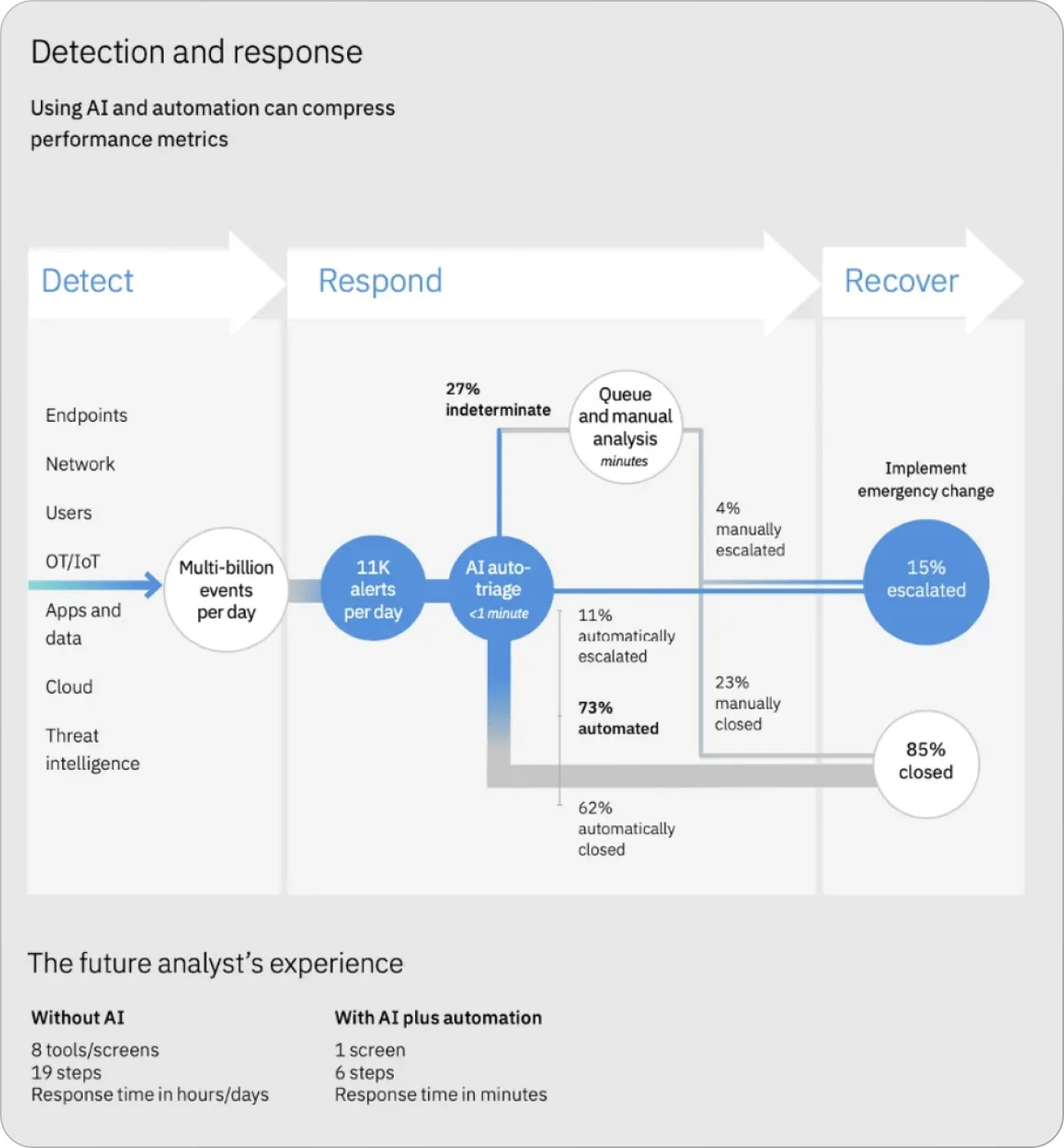
Architecture for AI-based automated threat detection and action engine (source)
As shown above, an AI-enabled automated threat detection solution can process billions of events of network requests, endpoints, users, and data points daily. All these events are processed in real time to provide instant analysis and take immediate action within minutes, compared to hours or days consumed due to manual threat detection.
AI in cybersecurity: Risks & challenges
Machine learning systems have done wonders for modern-day businesses by providing critical insights, aiding decision-making, and automating everyday cumbersome tasks. However, there are still many risks and challenges that need to be taken into consideration. Gaurav Keerthi, Deputy Chief Executive Officer at Cyber Security Agency of Singapore says that “AI holds great promise to provide solutions for mankind, yet from a cybersecurity perspective, AI can be both a blessing and a curse.”
Integrating AI in cybersecurity systems poses a number of challenges, such as:
Data manipulation. AI systems use data to understand historical patterns. Hackers can gain access to the training data, alter it to include biases and damage the efficiency of the models. Furthermore, data can be altered to benefit the hacker more.
AI-powered cyber attacks: Hackers can use AI techniques to develop intelligent malware that can modify itself to avoid detection from even the most advanced cybersecurity software.
Data unavailability: The performance of AI models depends on the volume and quality of data. If sufficient high-quality training data is not provided or the data contains bias issues, the AI system will not be as accurate as expected. Based on this data, an inadequately trained model will result in false positives and a false sense of security. Any threats will go undetected and lead to substantial losses.
Privacy concerns: To properly understand user patterns, AI models are fed real world user data. Without adequate sensitive data masking or encryption, user data is prone to privacy and security issues, favoring malicious actors.
Attacks on the AI systems: AI systems, like any other software product, are susceptible to cyber-attacks. Hackers can feed these models with poisonous data to alter their behavior according to their desired malicious intent.
However, all innovations are accompanied by concerns and skepticism. The right way forward is to build infrastructures that counter these risks as much as possible and provide a safe and secure environment for modern digital systems.
Final thoughts
Cyber threats are on the rise, both in terms of volume and complexity. Conventional cyber security systems need to catch up to modern malware and breaching tactics. This is why industry leaders are investing in AI technologies.
AI and ML-powered cybersecurity solutions are being developed that use extensive databases covering all known breach risks and malware types. These intelligent systems can detect malicious activities in real-time and can be programmed to issue immediate alerts and take automated actions.
Furthermore, machine learning models constantly learn about new threats, making them more efficient than manual detection techniques employed by human experts. With AI integration, the cybersecurity ecosystem is more robust than ever, offering enhanced security, shortening the time to react, and constantly adapting to new threats.
Check out our other articles on AI across industries: